Binary 101
The computer reads in a language called "Binary" Were "1's" and "0's" represent what the computer will see.
1=ON 0=OFF
1=1
2=10
4=100
8=1000
16=10000
32=100000
64-1000000
128-10000000
Now, the computer reads in a chart similar to this:
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
If you wanted to create a number such as "11" you would need to turn on the 8, the 2 and the 1 so it would look like:
00001011 (Which equals "11" in decimal form"
More Examples:
11111111=256
00000011=3
00010001=17
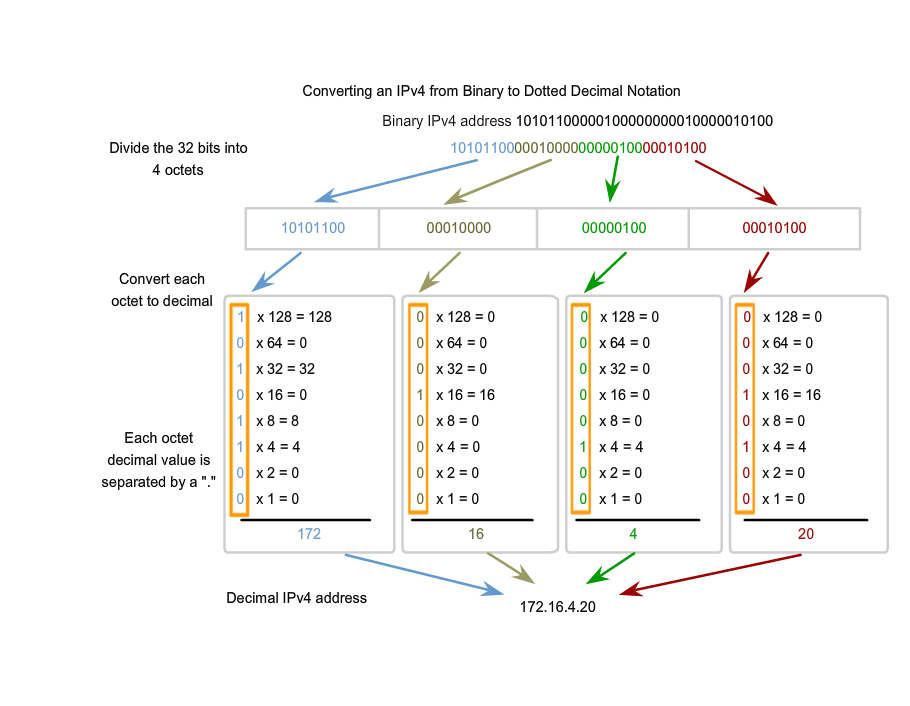
IP address and Binary
IP address are ussualy represented in decimal format, Separated each part of the address with a period by each octet (8 bits) All IP address are 32 bits long. Your standard class C address is in decimal form but has been converted from binary, So take your standard IP such as 67.128.127.13 and in an packet header it would be read as the following:
01000011.10000000.01111111.00001101
As a class C the bold part is the "Network" Portion of the IP address, while the rest is the "Host" Layer of the address.