Third Party Firmware
Introduction
In this article, you will be introduced to some of the third-party firmwares. Upgrading the firmware of your wireless router is one way to upgrade your wireless router because it will give you some rich feature. You may want to upgrade your want to update the firmware of your wireless router if you want your router to enhance some of the following features. The factory default firmware may or may not have these feature enable.
- Client mode or Client bridge mode
- Repeater mode or Repeater bridge mode
- WDM mode(Wireless Distribution System)
- bandwidth monitoring
- Virtual WLANs
- Advanced QoS
- IP and MAC filtering (including time and date)
- Filtering by web site and keyword
- Stability under heavy load
- Strengthens the signal and improves signal quality
- Enable VPN Services
- Enhanced Security: WPA and WPA2, both versions for Enterprise,
- Better customizable firmware and so on.
There are many kinds of third-party firmware available today. Here is a list of those third-party firmware available. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_wireless_router_firmware_projects. DD-WRT and Tomato are the most two popular ones because they are easy to install and configure. Another popular third-party firmware is OpenWRT, but it will no be discussed here because its configuration is more complex compare to DD-WRT and Tomato. Detail about OpenWRT can be found at http://wiki.openwrt.org
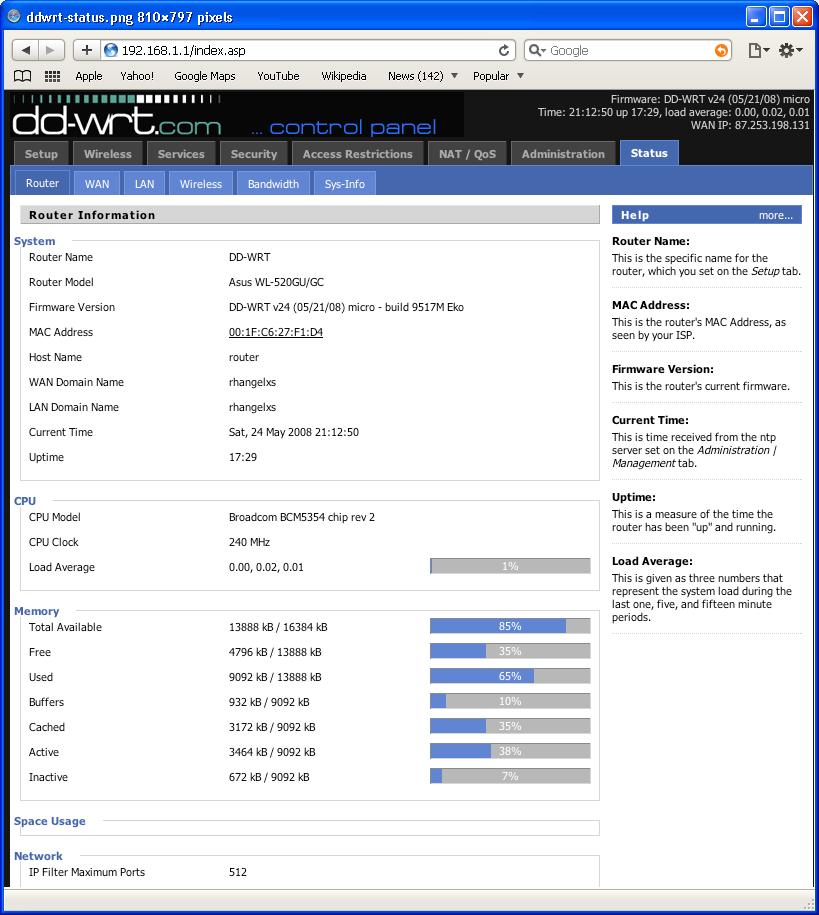
Screen shot of DD-WRT web interface:
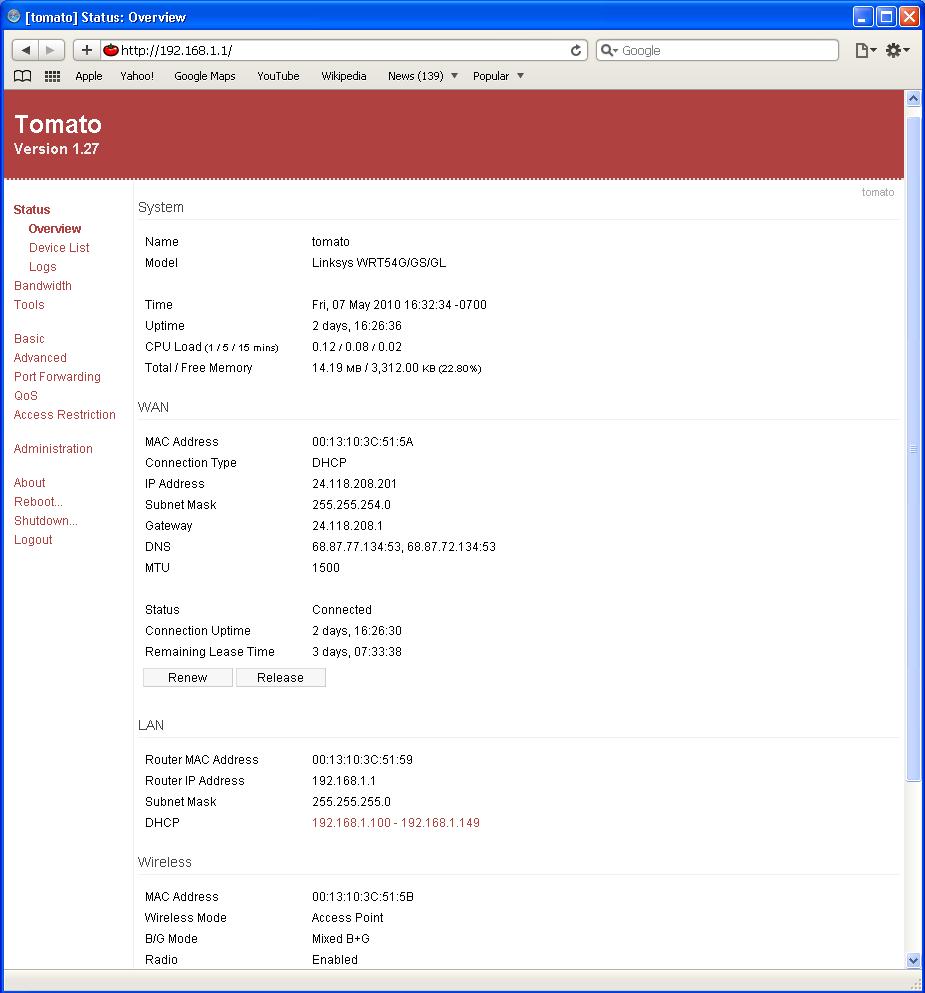
Screen shot of Tomato web interface:
DD-WRT is an alternate firmware available for many wireless routers. It is one of the most popular firmware. There is a paid and free versions available. DD-WRT is suitable for a great variety of WLAN routers and embedded systems.
Tomato is a free open source Linux-based firmware. The major emphasis of Tomato is on stability, speed and efficiency. Tomato includes several types of bandwidth usage charts, advanced QoS access restriction features, raised connection limits which enables P2P networking, and support for 125 High Speed Mode (marketed by Linksys as "SpeedBooster").
In the section below, I will guide you to the processes of downloading and installing DD-WRT firmware. It just a brief instruction to DD-WRT firmware. Following this instruction at your own risk. I will not responsible for any cause or damage. If you need more specific detail or instruction of DD-WRT, go to http://www.dd-wrt.com.
DD-WRT Instruction
- NOTE: Downloading and installing DD-WRT firmware is easy. However, do it improperly can damage your router, and make it unusable.
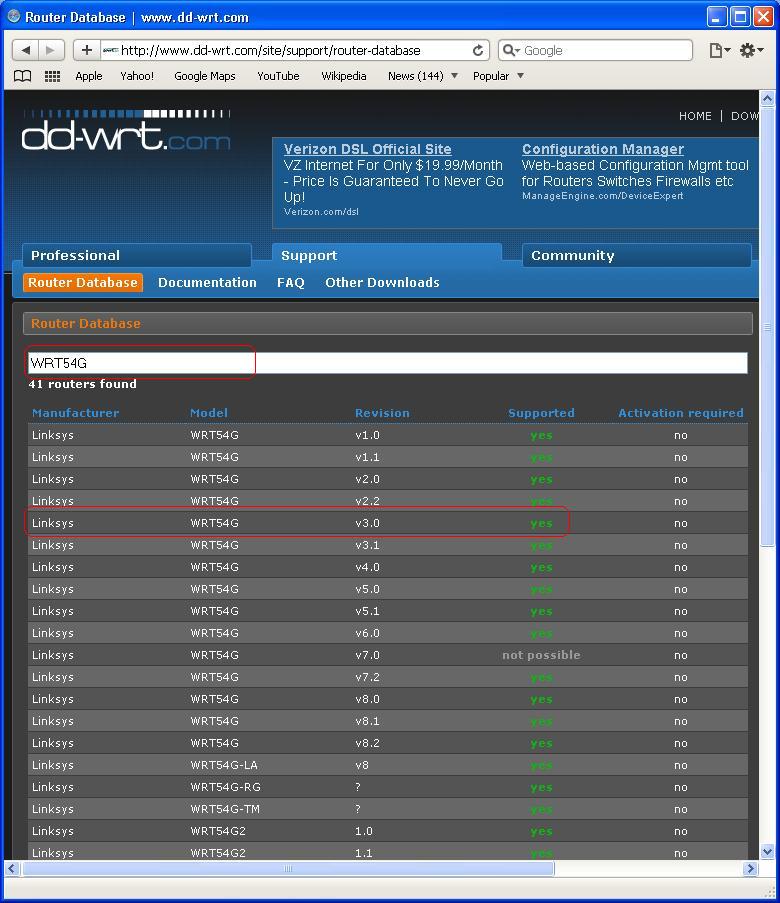
Before downloading the firmware images, check your router's model, version and the manufacture. These informations can be found on the back of your router. In this guide, I will use Linksys's model WRT54G Version 3.0.
Downloading
Follow the steps below to download DD-WRT firmware files.
- 1st step
Go to http://www.dd-wrt.com/site/support/router-database, and type you router's model, name, manufacturer and/or revision in the long search box. If you have a supported router, you router's Manufacturer, Model and Version should appear right below the search box. Click on the correct model and version.
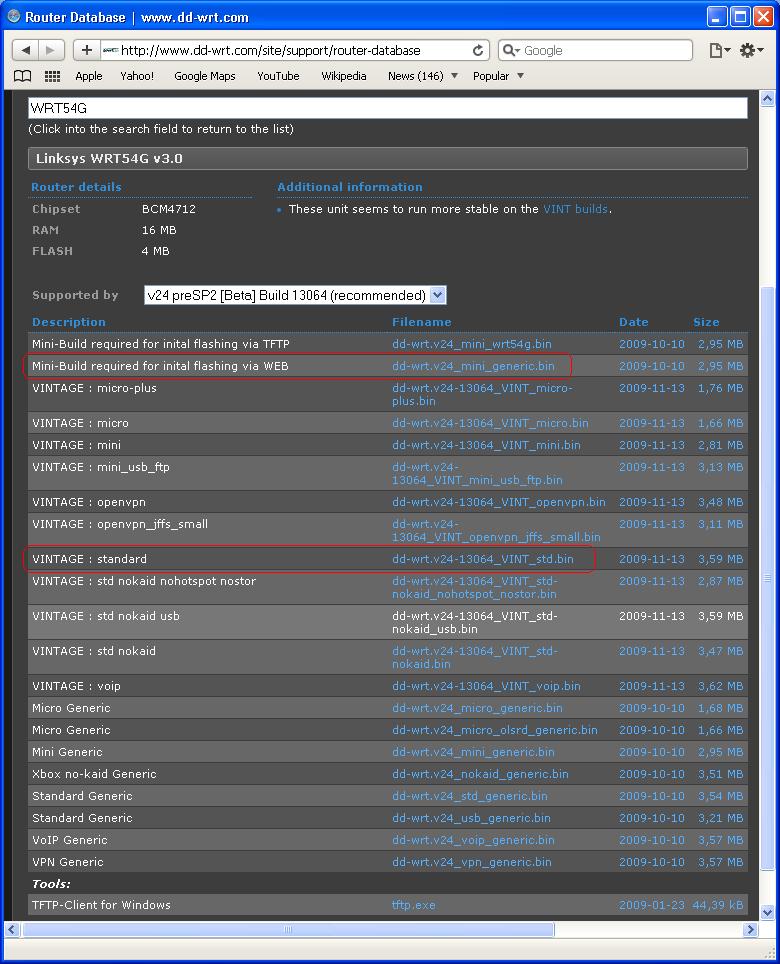
- 2nd Step
You may need to download multiple files. For my WRT54G, I will download the dd-wrt.v24_mini_generic.bin and dd-wrt.v24-13064_VINT_std.bin and save to a folder called "firmware" on Desktop. The first image, dd-wrt.v24_mini_generic.bin, is required by WRT540 before it can be installed or flashed to any other feature build on image file. The second image, dd-wrt.v24-13064_VINT_std.bin, is a standard build on.