Securing Router Logins with SSH
Securing Router Logins with SSHThis is a walk through to help new students learn how to configure a more secure login with a router and utilize SSH.
Checking Router Bin file
This is a check to ensure that the router you are using is going to run SSH.
- Step 1
Issue the command show flash, to check and see if K9 is in the bin file
Router Configuration
This will cover the commands needed to setup the router logins and SSH.
- Step 1
enaable
- Step 2
config t
- Step 3
hostname (name)
- Step 4
security passwords min-length (number), we used 10 for a password length of 10 characters.
- Step 5
eable secret (password)
- Step 6
no enable password to clear passwords that may already be set.
- Step 7
user (name) secret (password) this will be your user name and password for loging in to the router and SSH.
- Step 8
line console 0 login local
- Step 9
line aux 0 no password login local
- Step 10
line vty 0 4 login local transport input ssh this last command is to use ssh and not telnet.
- Step 11
ip domain-name (domain name)
- Step 12
cry key generate rsa (360-2048) you will use this to set the size of the key the larger the more secure.
- Step 13
ip ssh time-out (number) ip ssh authentication-retries (number)
Examining Capture Data
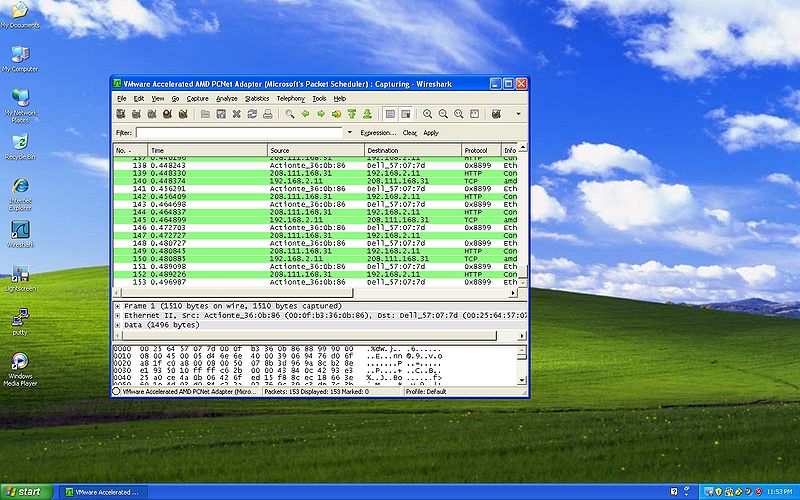
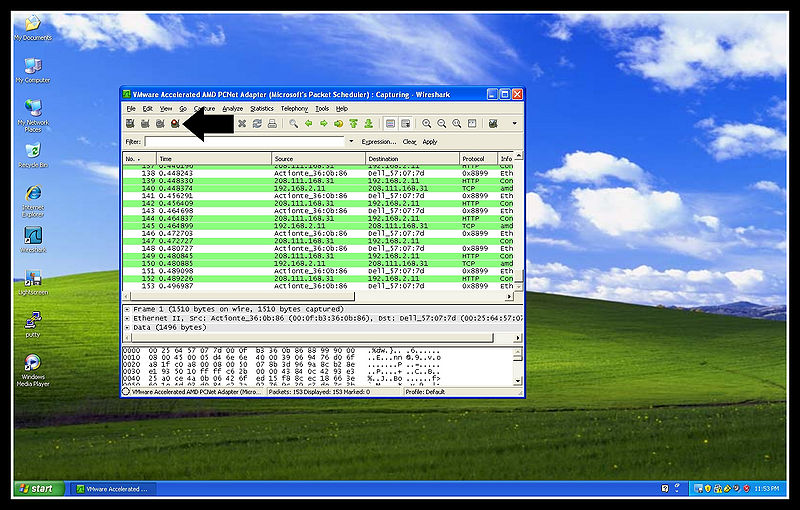
In this section we will be showing you how to capture protocols and where to locate the important values given by the use of wireshark.
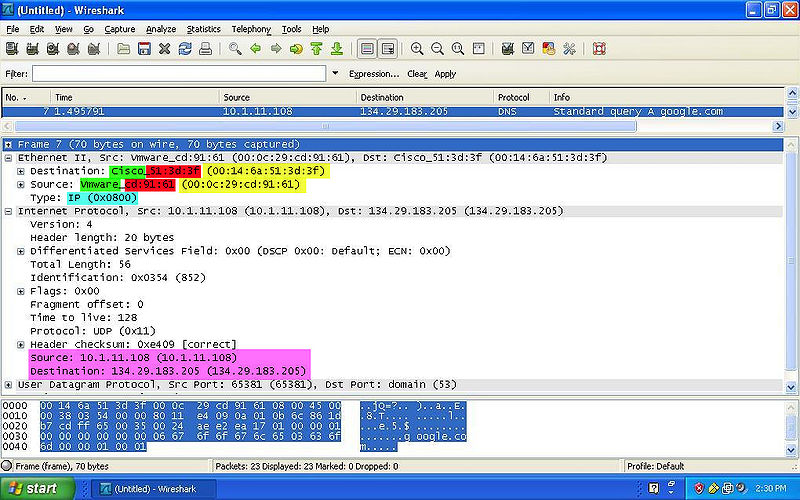
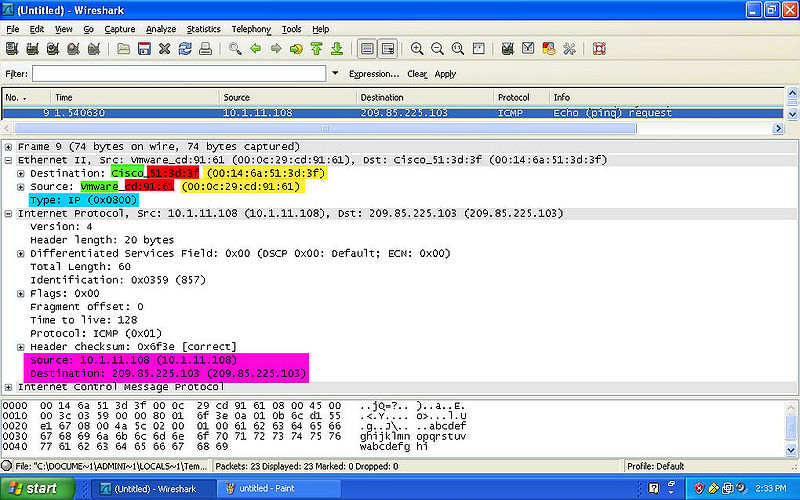
Color Code
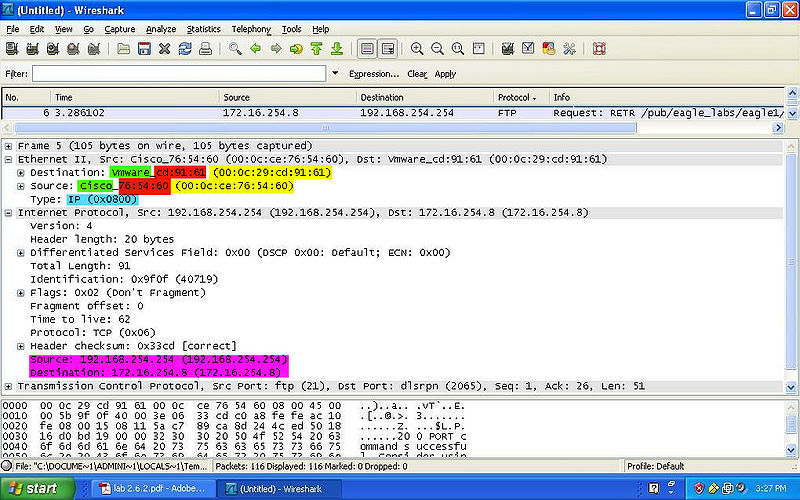
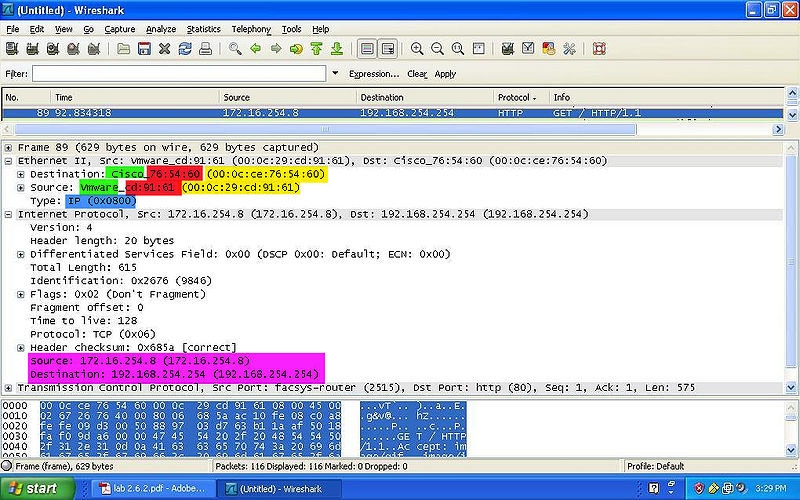
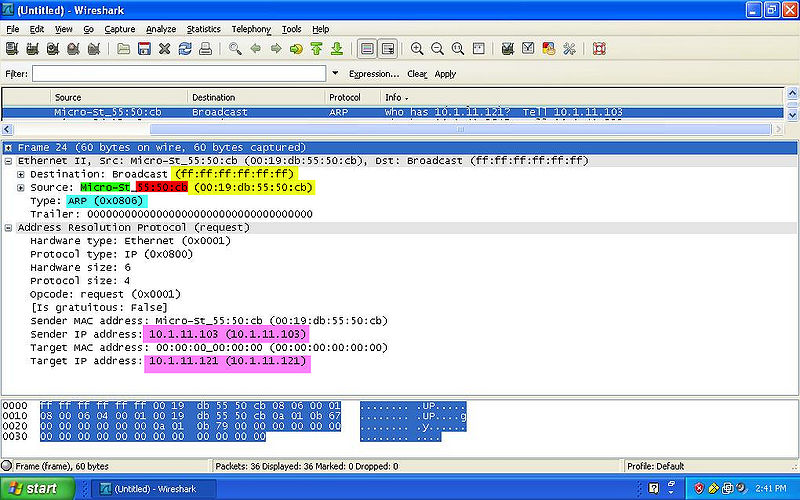
- YELLOW: Indicates the MAC Address of both the destination and source.
- GREEN: Indicates the NIC Manufacturer of both the destination and source.
- RED: Indicates the NIC Serial Number of both the destination and source.
- BLUE: Indicates the Frame Type of the packet.
- PINK: Indicates the IPv4 of both the destination and source.
- NOTE: The the Preamble and the FCS are NOT shown on wireshark.
FTP
HTTP
ARP
DNS
ICMP
Creating a Shortcut to Auto Run Wireshark
In this section we will be showing you how to create a new desktop icon to auto start your wireshark and have it select the correct network adapter and start capturing by simply double clicking the new icon.
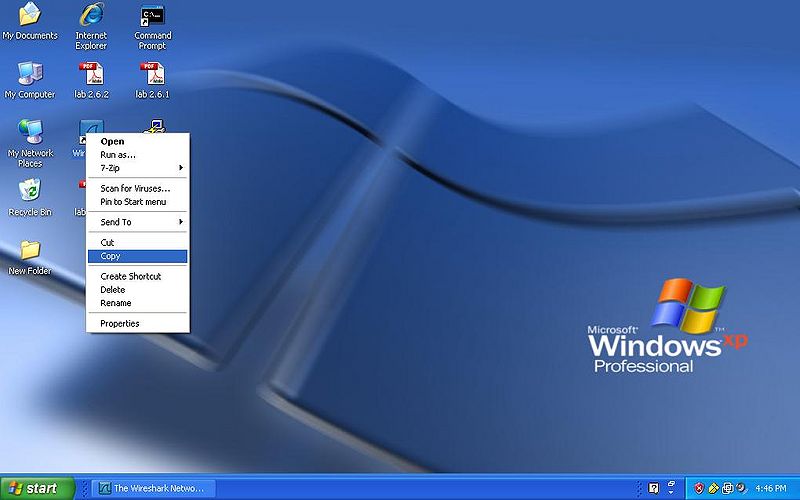
- Step 1
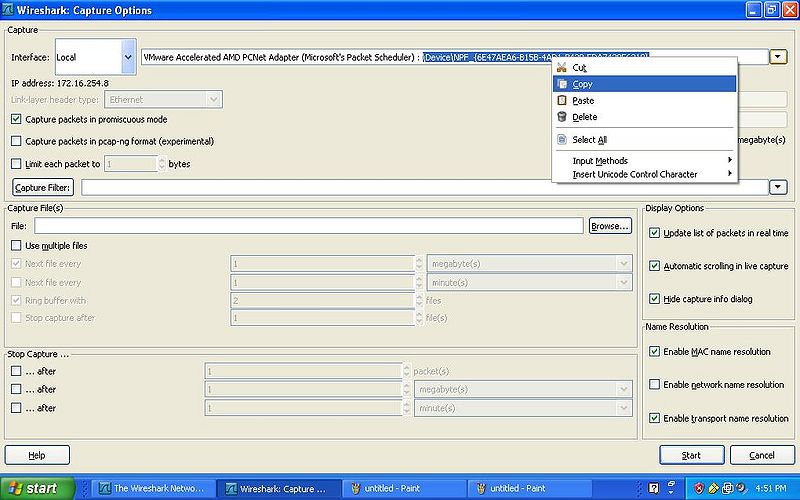
Right click the Wireshark icon and click copy.
- Step 2
Right click on the desktop and click paste.
- Step 3
Right click the new icon and rename "Wireshark Auto Start"
- Step 4
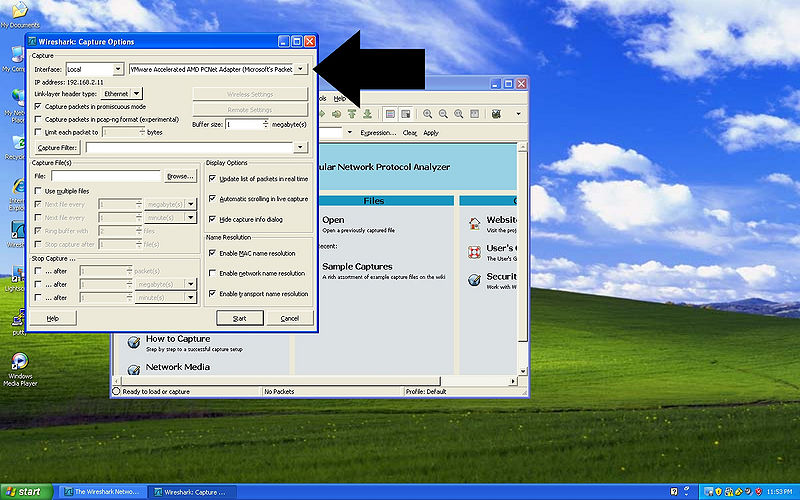
Open Wireshark and click on the Capture Options go to the pull down as previously mentioned and select the VMware network adapter, open the window fully to see the path and select everything after the after the : you should have this selected \Device\NPF_{numbers} as seen in the picture.
- Step 5
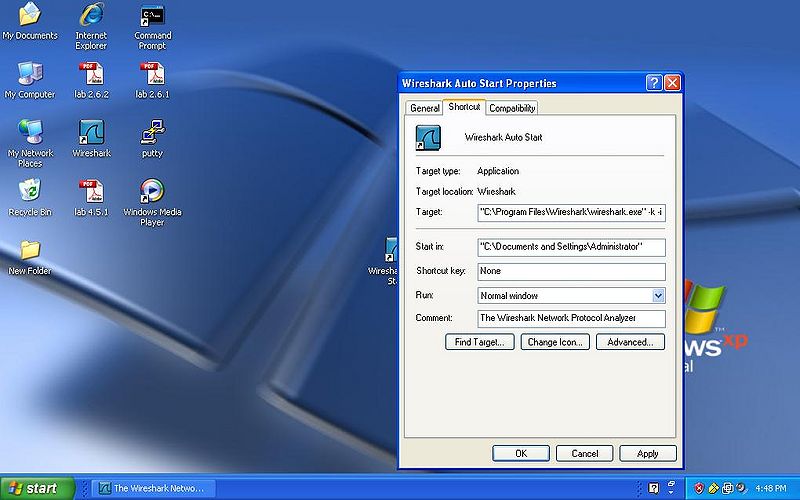
Right click and click properties on the NEW Wireshark icon, and add this to the end of the target line -k -i
- NOTE: You need to have a space before the -k and after the -i.
- Step 6
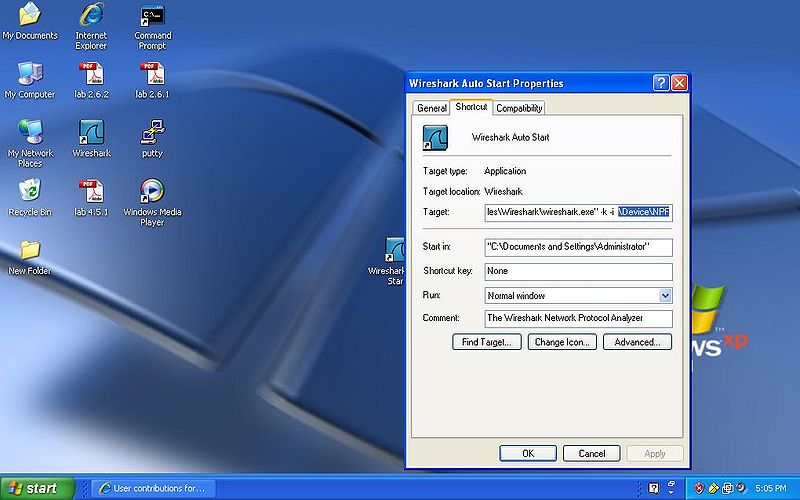
Now after the -i "and the space" paste the \Device\NPF_[numbers} to the target line as shown in the picture.
- Step 7
Click on the Ok button and now you can simply double click the new icon to start Wireshark and select your network adapter and begin capture with one click of the button. Enjoy!!!