Chapter 2 Study Guide
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Linux Installation and Usage
- ^ Preparation and installation of Fedora Linux using good practices.
- ^ Outline the structure of Linux interface.
- ^ Enter basic shell commands and find command documentation.
- ^ Properly shutdown the Linux OS
Preparing for Installation
- Hardware Compatibility List (HCL)
- The minimum requirement s for Fedora 13 Linux can be found :
- Preinstallation checklist
- A system checklist that can compared against the HCL during installation.
- Information will include :
- • CPU (Type /MHz)
- • RAM (Mb)
- • Keyboard model and layout
- • Hard Disk size (MB)
- • Host Name
- • Network card IP configuration
- • IP address, Netmask Gatway, DNS servers, and DHCP
- • Linux Packages to install
- • Video Card Make and Model
- • Video Card RAM (Mb)
- • Monitor make and model
- • Monitor Vsync and HSync ranges
Installation Methods
- FTP server across network
- HTTP web server across network
- NFS server across network
- SMB (SAMBA) server across network
- Packages located on HD
- CD-ROM or bootable DVD media
Performing the Installation stages
- Start installation
- Choosing language, keyboard and storage type
- Selecting hostname, time zone & root password
- Configuring storage devices
- Configuring the boot loader
- Selecting and installing packages
- Completing first boot wizard
Starting the Installation
- System Rescue – A installation feature used to repair a system from the installation DVD
- Can be used to repair a Linux system which cannot be started.
- Memory Test – Can be used to test memory and prevent errors. Uses memtest86 utility to test RAM for errors
Checking media for errors
- Feature of the default installation
- Optional - Good practice with new, unused media
- Checks bootable DVD or CD-ROM for errors
Choosing language, keyboard and storage type
- This is just a matter of choosing the language you’ll be using,
- your default keyboard layout and whether or not you’ll installing Linux locally or on a DASD (direct access storage device)
Configuring Storage Devices
- Can only be one of four basic configurations:
- Primary master PATA - had
- Primary slave PATA – hdb
- Secondary master PATA – hdc
- Secondary slave PATA – hdd
- Used by newer server systems typically use :
- SATA/SCSI –1st disk= sda, 2nd disk = sdb, 3rd disk= sdc, ect.
- Unlike PATA can have more than four hard disks
Hard Disk Partitioning
- Maximum of four primary partitions
- Extended Partition can contain unlimited number of smaller partitions or logical drives
- Root Directory (\)
- Swap memory – Virtual memory utilized when physical memory (RAM) is being exhausted
Primary Master Partitioning
- Linux only requires two partitions minimum :
- Root directory (main directory) designated by a “\”
- Swap (aka Virtual memory)
- NOTE : Doesn’t contain a file system and is never mounted to a directory because Linux is responsible for swapping info.
- Extra partitions help keep the entire system free from errors.
Basic Linux
- Kernel – Loads all components and controls computing activities, the heart of the operating system
- Once the BIOS starts after boot-up, it then starts a boot loader (such as GRUB) which then loads the Linux Kernel into memory.
- If there is a windows system already on the HD the boot loader can give you the option of which OS you’d like to load. This is known as dual booting.
- Terminal – Channel that allows users to log in
- Shell – Passes user input to the kernel for processing. BASH shell (Bourne Again Shell) – command-line shell similar to cmd on Windows
Basic Shell Commands
- Commands – Case sensitive, indicate program to execute
- Options – specific letters preceded by a hyphen (-) following a command
- Arguments – specify parameters that tailor the command to the users particular needs
- Command line order is this.. (Command) (Options)(Argument)
- Ls – a /etc/ntp
- Command = Ls (list)
- Option = -a (lists all files)
- Argument = /etc/ntp (refers to the /etc/ntp directory)
Common Commands
- You can find some common commands on page 66 of the text.
Metacharacters
- Keyboard characters that have a special meaning
- ($) – Tells the shell that the following text refers to variable
- A piece of information that is stored in memory, typically uppercase words, automatically set by the Linux system at login
- There’s a list of metacharacters used in BASH on page 67 of the text
Help
- Manual pages (man pages)
- man <command name>
- Include description, syntax, options, related files, and commands
- Search manual pages with a keyword use –k
- man –k <keyword>
- Info pages – include easy-to-read description and hyperlinks
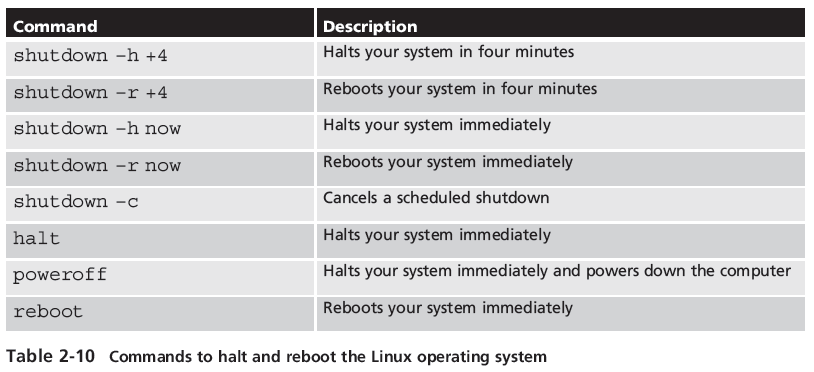
Shutdown Commands
- Here is a list of various shutdown commands which can be found on page 73 of the text
Credit
All info compiled, edited and coded by : Rob Klaers, Clay Wilson, Michael Garin, & Todd Bailly
NOTE : all page numbers reference the Linux+ Guide to Linux Certification 3rd Ed. by Jason W. Eckert ISBN 978-1-4188-3721-1