Modifying Permissions With ICACLS: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
/Q indicates that icacls should supress success messages. | /Q indicates that icacls should supress success messages. | ||
*ICACLS preserves the canonical ordering of ACE entries: | |||
Explicit denials, Explicit grants, Inherited denials, Inherited grants | |||
*Perm is a permission mask and can be specified in one of two forms: | |||
a sequence of simple rights: | a sequence of simple rights: | ||
F - full access | F - full access | ||
| Line 34: | Line 33: | ||
R - read-only access | R - read-only access | ||
W - write-only access | W - write-only access | ||
a comma-separated list in parenthesis of specific rights: | a comma-separated list in parenthesis of specific rights: | ||
D - delete | D - delete | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
RA - read attributes | RA - read attributes | ||
WA - write attributes | WA - write attributes | ||
inheritance rights may precede either form and are applied | |||
inheritance rights may precede either form and are applied only to directories: | |||
(OI) - object inherit | (OI) - object inherit | ||
(CI) - container inherit | (CI) - container inherit | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
(NP) - don't propagate inherit | (NP) - don't propagate inherit | ||
Examples: | * Examples: | ||
icacls c:\windows\* /save AclFile /T | icacls c:\windows\* /save AclFile /T | ||
Revision as of 20:09, 17 July 2010
Modifying Permissions With ICACLs
- Purpose
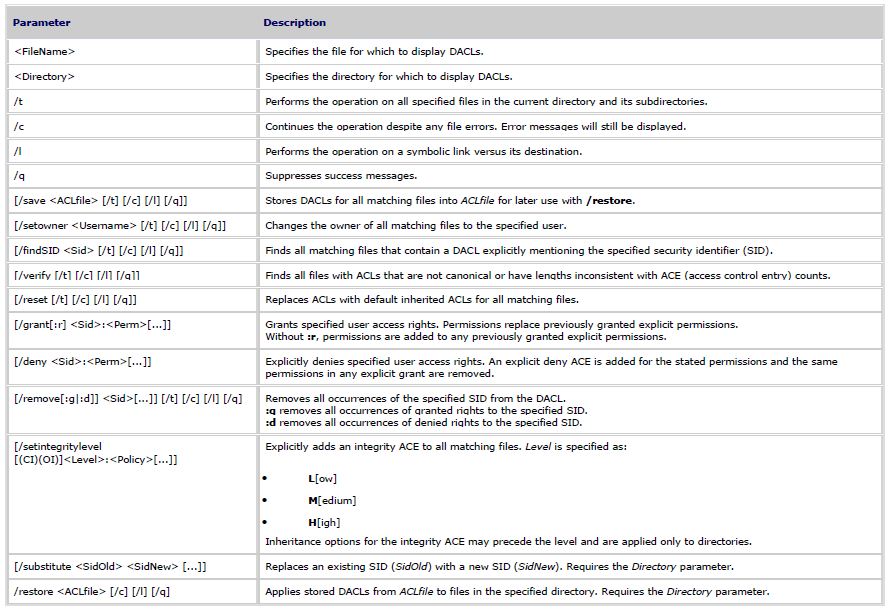
Displays or modifies discretionary access control lists (DACLs) on specified files, and applies stored DACLs to files in specified directories. This can be used with Windows Server 2008 Server Core where no GUI exists.
- Syntax
icacls <FileName> [/grant[:r] <Sid>:<Perm>[...]] [/deny <Sid>:<Perm>[...]] [/remove[:g|:d]] <Sid>[...]] [/t] [/c] [/l] [/q] [/setintegritylevel <Level>:<Policy>[...]]
icacls <Directory> [/substitute <SidOld> <SidNew> [...]] [/restore <ACLfile> [/c] [/l] [/q]]
Note: Sids may be in either numerical or friendly name form. If a numerical form is given, affix a * to the start of the SID.
/T indicates that this operation is performed on all matching files/directories below the directories specified in the name.
/C indicates that this operation will continue on all file errors. Error messages will still be displayed.
/L indicates that this operation is performed on a symbolic link itself versus its target.
/Q indicates that icacls should supress success messages.
- ICACLS preserves the canonical ordering of ACE entries:
Explicit denials, Explicit grants, Inherited denials, Inherited grants
- Perm is a permission mask and can be specified in one of two forms:
a sequence of simple rights:
F - full access
M - modify access
RX - read and execute access
R - read-only access
W - write-only access
a comma-separated list in parenthesis of specific rights:
D - delete
RC - read control
WDAC - write DAC
WO - write owner
S - synchronize
AS - access system security
MA - maximum allowed
GR - generic read
GW - generic write
GE - generic execute
GA - generic all
RD - read data/list directory
WD - write data/add file
AD - append data/add subdirectory
REA - read extended attributes
WEA - write extended attributes
X - execute/traverse
DC - delete child
RA - read attributes
WA - write attributes
inheritance rights may precede either form and are applied only to directories:
(OI) - object inherit
(CI) - container inherit
(IO) - inherit only
(NP) - don't propagate inherit
- Examples:
icacls c:\windows\* /save AclFile /T
- Will save the ACLs for all files under c:\windows and its subdirectories to AclFile.
icacls c:\windows\ /restore AclFile
- Will restore the Acls for every file within AclFile that exists in c:\windows and its subdirectories
icacls file /grant Administrator:(D,WDAC)
- Will grant the user Administrator Delete and Write DAC permissions to file
icacls file /grant *S-1-1-0:(D,WDAC)
- Will grant the user defined by sid S-1-1-0 Delete and Write DAC permissions to file