Packet Tracer Instructions
Packet Tracer Instructions
Cisco Packet Tracer is a powerful network simulation program that allows us to create a network with an almost unlimited number of devices, encouraging practice, discovery, and troubleshooting. The main objective of Packet Tracer is to serve as a support tool for the Cisco Academy. This tool is extremely useful for both students and teachers. In this page, I will walk you step by step through the process of downloading/install and building a network using Packet Tracer. This instruction is best for students who have accounts to access Cisco Networking Academy home page.
Downloading & Installing Packet Tracer
Packet Tracer 5.2 is the latest version of Cisco's simulation software available. To download Packet Tracer, follow the instruction below:
How to download
- Step 1
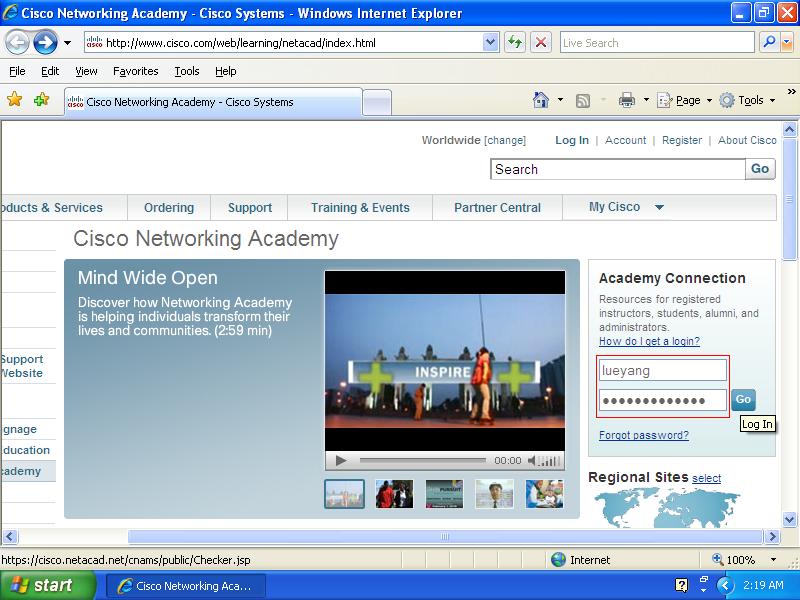
Go to Cisco Networking Academy home page
(NOTE: Make sure to hold Ctrl key to open the link in a new tab.)
- Step 2
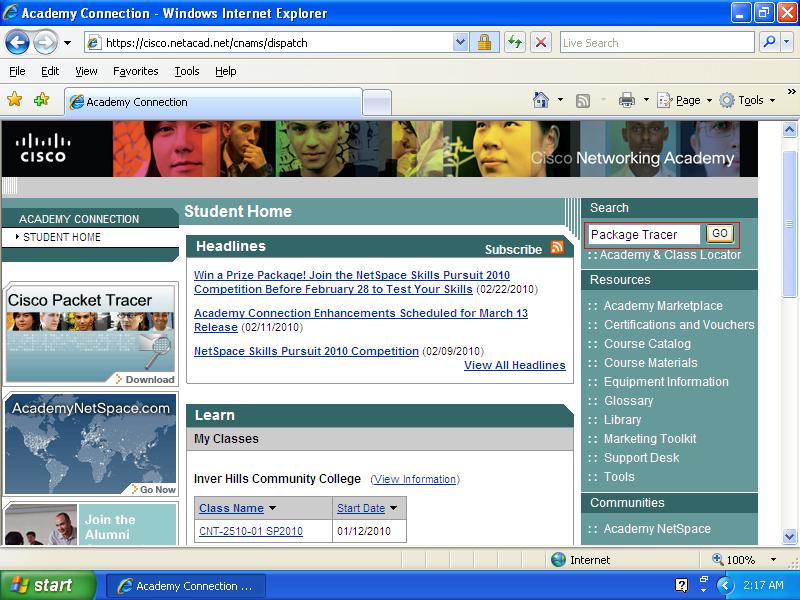
Login onto the Student Home using your username and password.
- Step 3
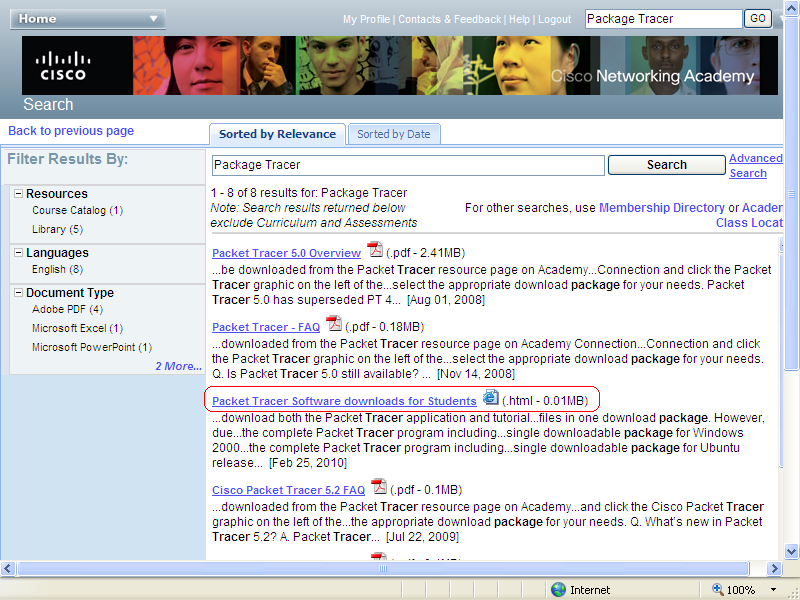
On the Student Home page, type Packet tracer in the search box and press Enter key or click on the GO bottom to search for the software.
- Step 4
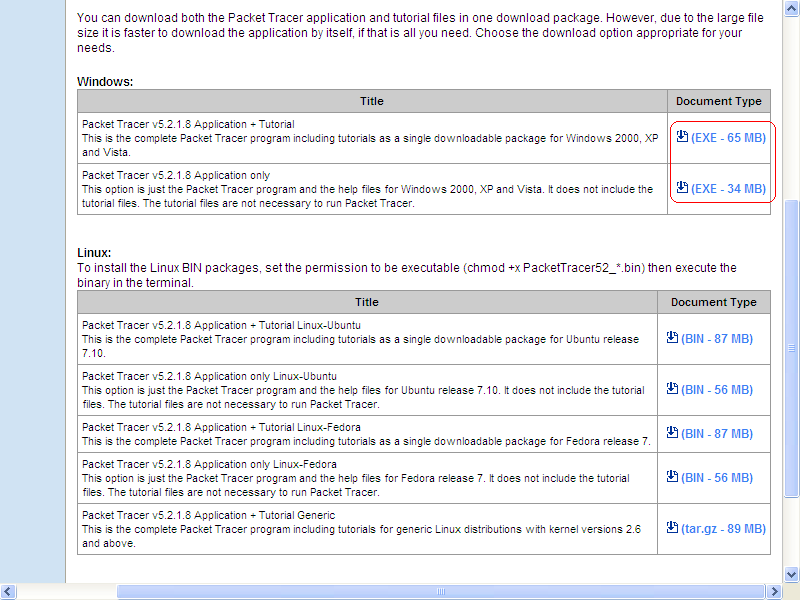
Scroll down to find Packet Tracer Software downloads for Students (.html - 0.01MB). Click on the link and you will see the search as show bellow.
- Step 5
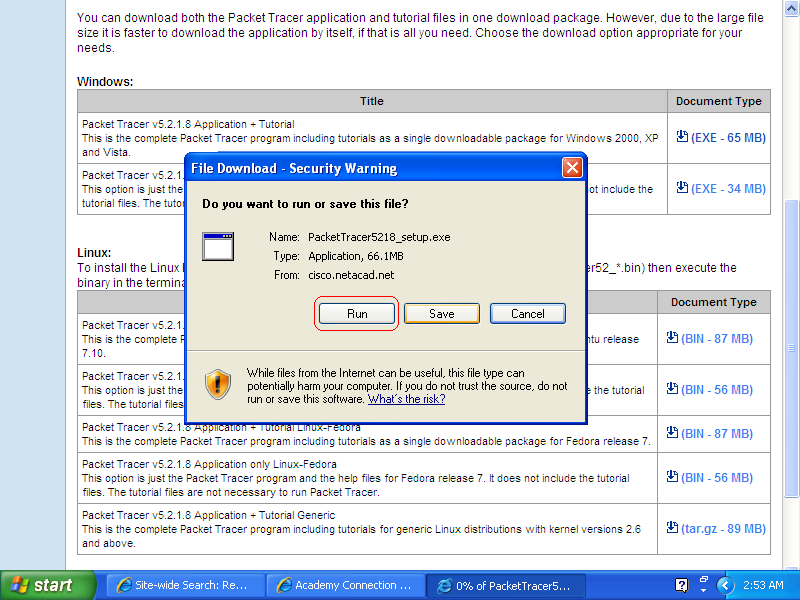
To download, click on (EXE - 34 MB) save it on your Desktop.
Next section will walk you through the process of installing Cisco Packet Tracer.
Installation
After downloading is completed, follow the steps bellow.
- Step 1
To install Cisco Packet Tracer, double click on the PacketTracer5218_setup_no_tutorials.exe file on your desktop.
And, then click Run to run the installation process.
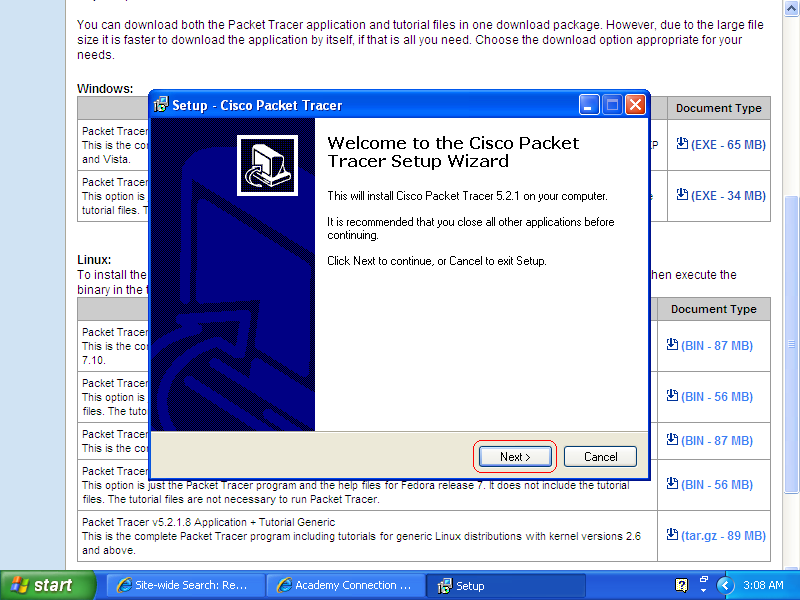
- Step 2
Click next
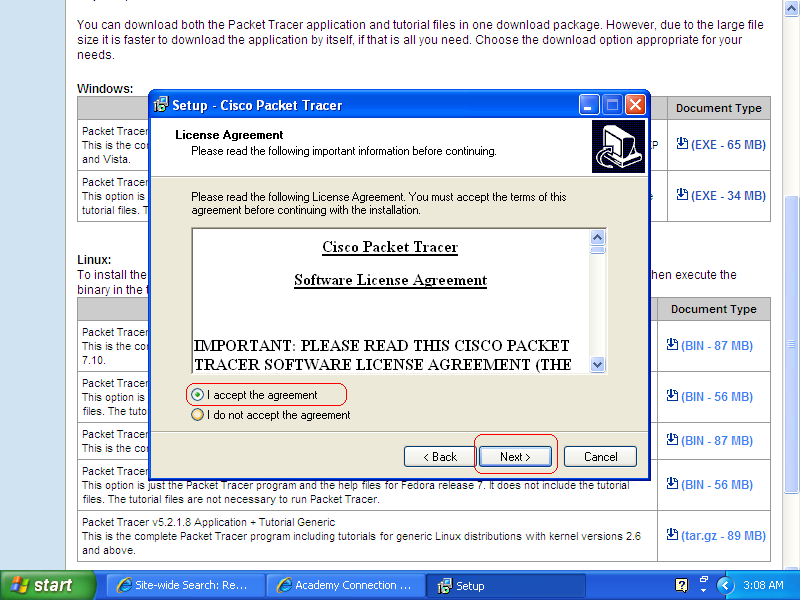
- Step 3
In oder to install the software, you must check I accept the agreement and then click Next button.
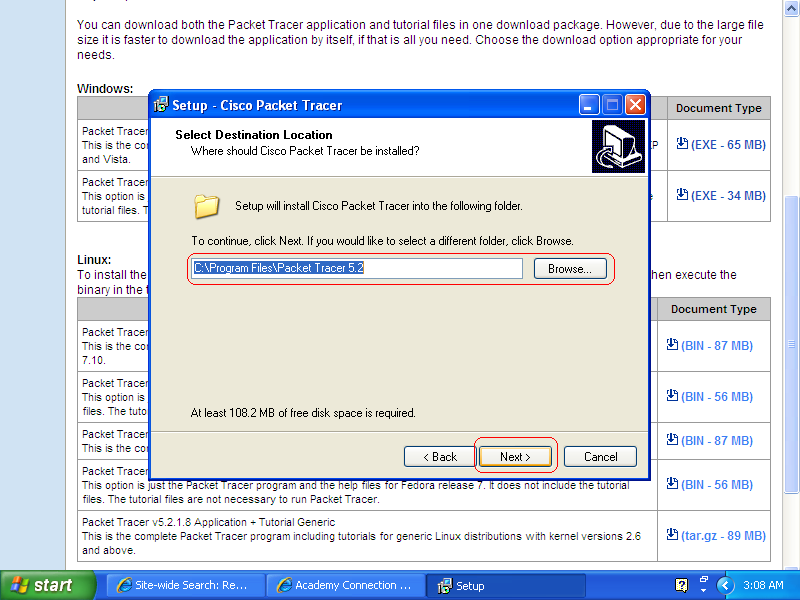
- Step 4
Click Next button until the installation process is finished.
- Step 5
Click the Finish button.
Now you are completed with installation process. The next section will be showing you how to use Cisco Packet Tracer.
Using Cisco Packet Tracer
This section will show you how to use Packet Tracer by creating a basic network environment.
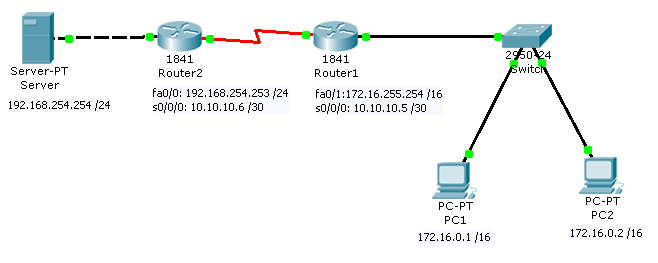
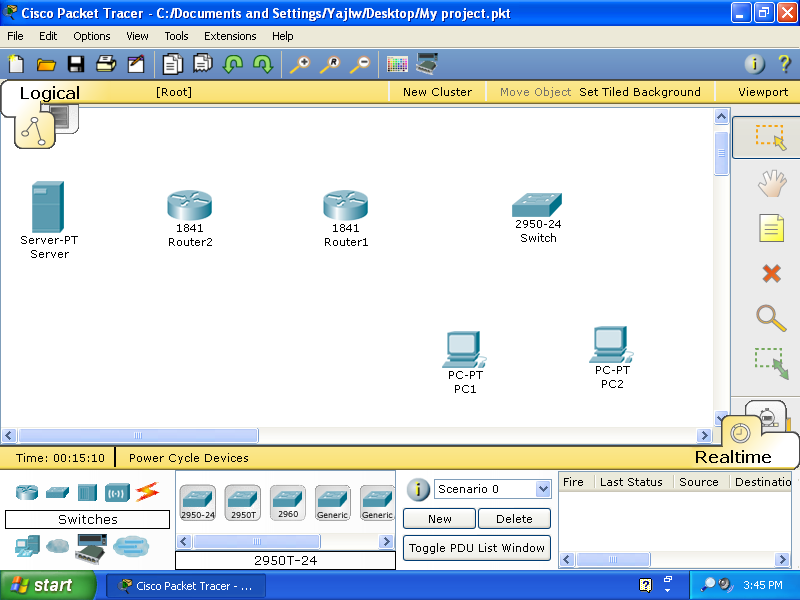
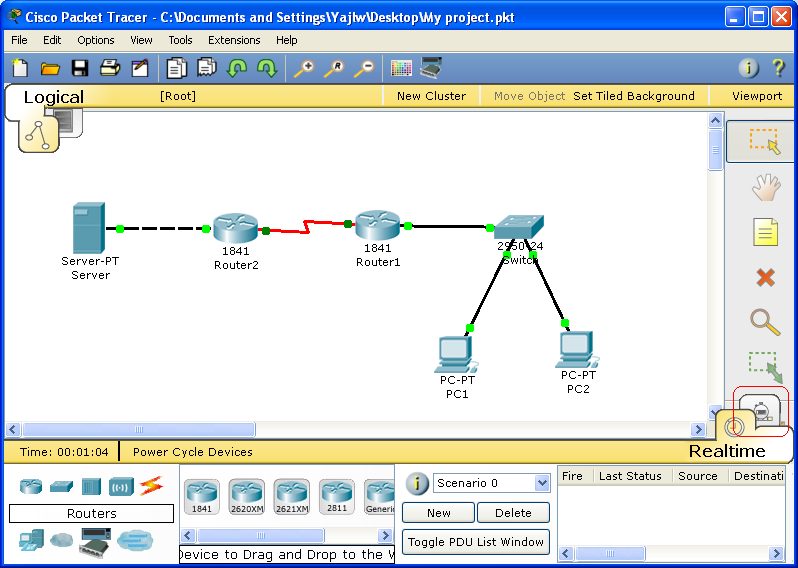
Below is the topology diagram of the network. The IP address and Subnet mask in this topology will be using to configure the network connection in the next section.
Creating Cisco Network Devices
Follow the steps bellow to create the network devices base on the topology above.
- Step 1
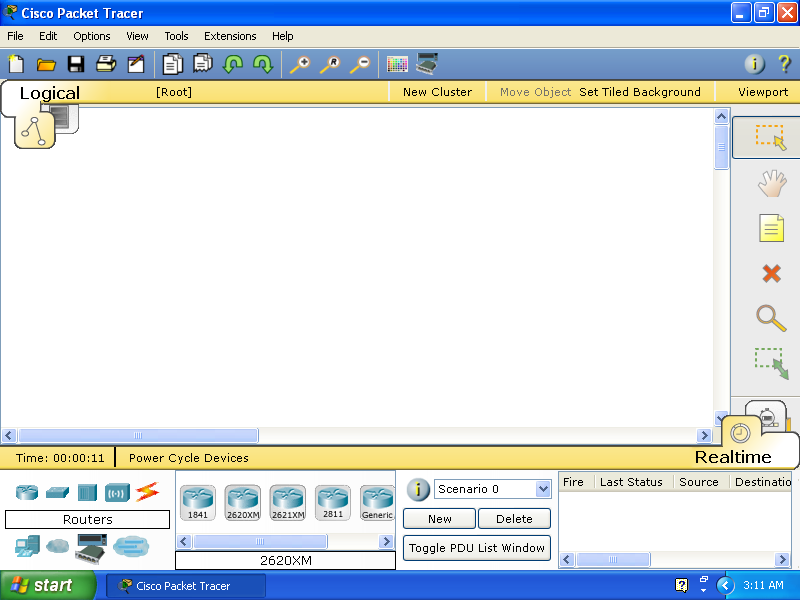
Double click the Cisco Packet Tracer icon on your Desktop to run Cisco Packet Tracer.
Cisco Packet Tracer' windows interface:
- Step 2
A router is created by clicking on Routers icon that locates on the bellow left-hand conner, and the routers with its model names will appear next to the right. Click and draft the 1841 Router to the work area, and chang the name to Router1. Changing the router's name is optional. Create another router and name it Router2.
- Step 3
Follow the step above to create the Switches, PC1, PC2, and the Server.
- Step 5 Adding Cisco Router's modules
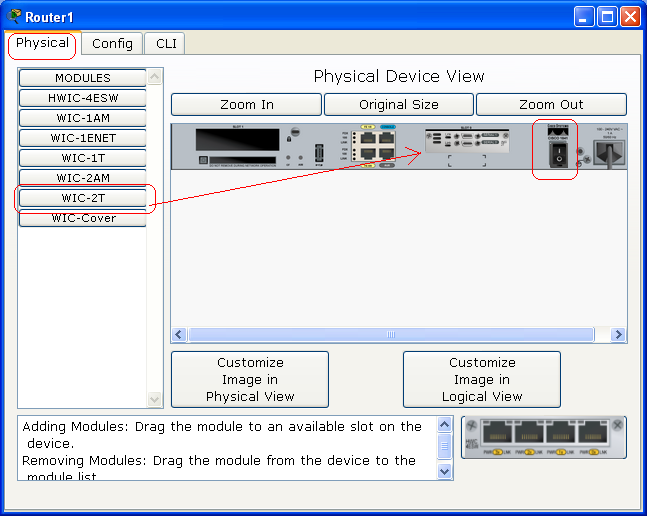
Click on Router1, and under Physical tab, you will see the picture of the router's interface under "Physical Device View". Turn the power off, and then click and draft the WIC-2T module to the second slot of the expansion slots of the router. Turn the power of the router back on.
- Step 6Follow the same step above to add a module for Router2.
Connecting and Cabling
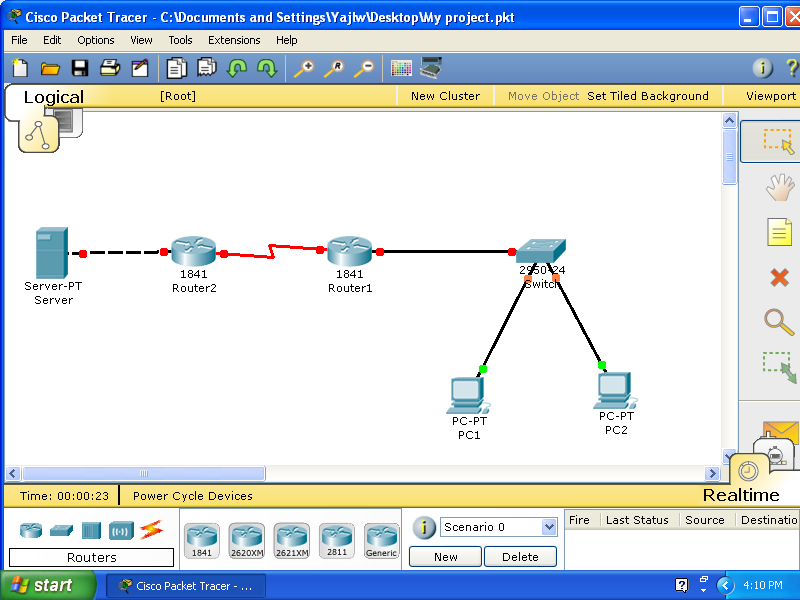
To connect all the devices together, click the Connection icon, and then click the cable icon next to the right to choose the right cable.
- (Note) Make sure to choose the right cables.
From PC1, PC2 and Router1 to the Switch, use Copper Straight-Through cables to make connection. Between Router1and Router2, use Serial cable (DCE). And, between the Router2 and Server, use Copper Cross-Over cable.
Connection should be like this:
Configuring Devices
To make communication between the device, each device needed to be configured correctly.
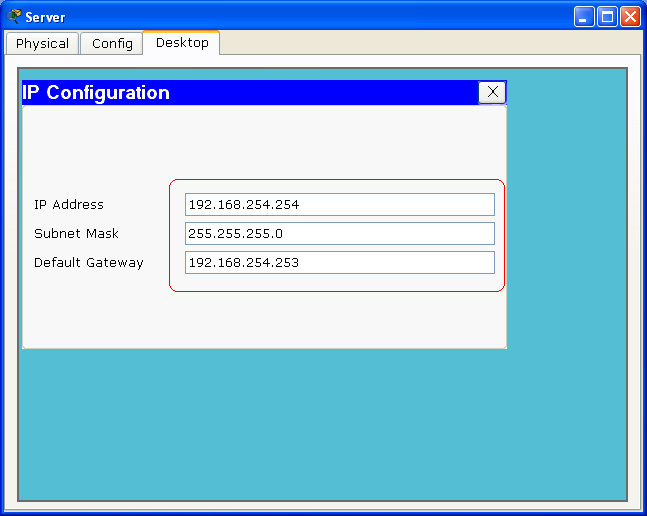
- Configuration for the Server:
First, click on the Server and make sure the power is on. Under Desktop tab, click on the IP Configuration icon, and input the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway as shown bellow. Click the red X of the Sever Windows to close the configuration.
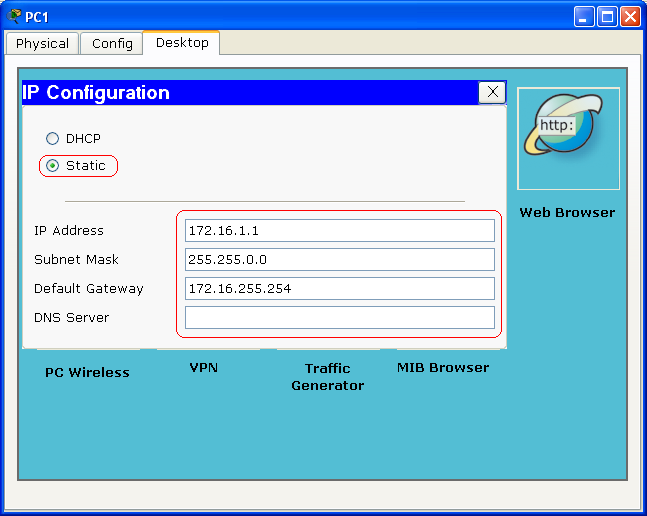
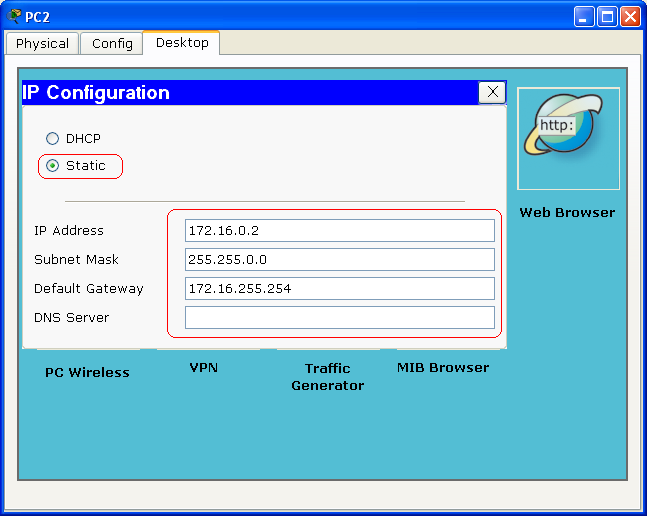
- PC1 and PC2 are Configured using the same step of Configuration for the Server above.
- Configuring Router1:
Now you have all the end devices configured. The next step is to configure the two routers.
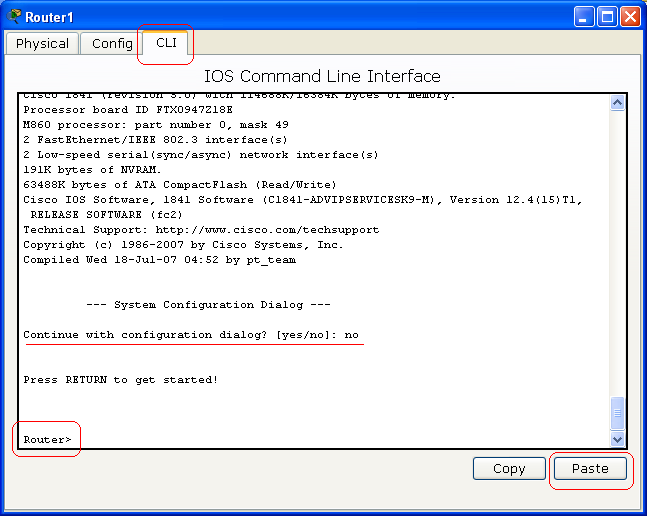
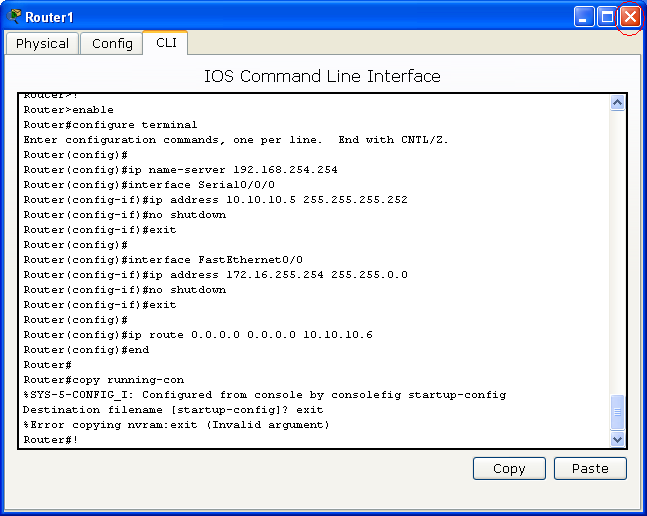
Click on the Router1, make sure that the power of the router is on, and then click on the CLI tab. If you see a question says "Continue with configuration dialog? [yes/no]:" type no and press Enter key. Press Enter key couple times until you see "Router>".
When you see "Router>", copy the command bellow, including the "!", and past the command into the Router1 CLI windows by clicking on the Paste bottom.
!
enable
configure terminal
ip name-server 192.168.254.254
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 10.10.10.5 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
exit
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 172.16.255.254 255.255.0.0
no shutdown
exit
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.6
end
copy running-config startup-config
!
After you paste the command above to the CLI windows, you should see some text like this:
Close this windows.
- Configure Router2: Router2 use the same configuration step as Router1 and use the following command:
!
enable
configure terminal
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.254.253 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
exit
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 10.10.10.6 255.255.255.252
clock rate 64000
no shutdown
exit
ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 10.10.10.5
end
copy running-config startup-config
!
After you done pasting the above command into the Router2 CLI windows, close the windows.
Now you are done with the configuration. You can save your project for later use.
Examining Devices Communication
In this section I will use the ping and tracert or traceroutcommand to examining the network connectivity to make sure that every device on the network can communicate with each other properly.
In this section, we are examining the communication between PC1 and server.
Realtime Mode
Use the Realtime Mode to test network connectivity in realtime.
- Examining by using ping and tracert commands
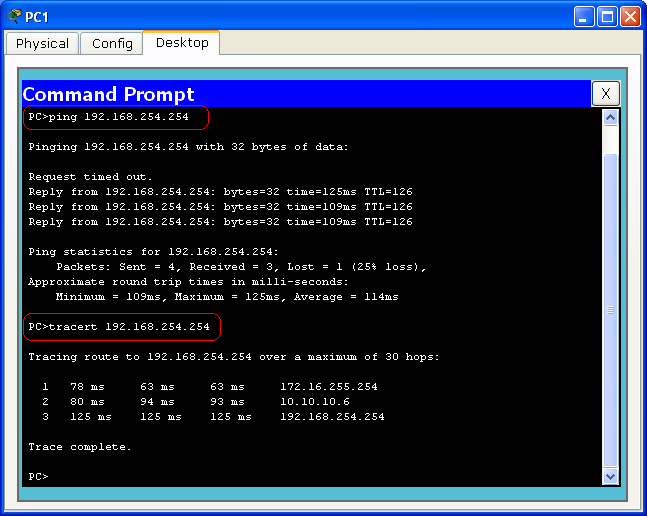
Click on PC1, and under Desktop tab, click on the Command Prompt or Run icon and the command prompt will open. Type ping 192.168.254.254 and press Enter key to see if PC1 can communicate with the Server. Type ping 192.168.254.254 to see how PC1 can route the packets to the Sever. Bellow is an example of the ping and tracert command output.
- Examining by using Web Browser(HTTP)
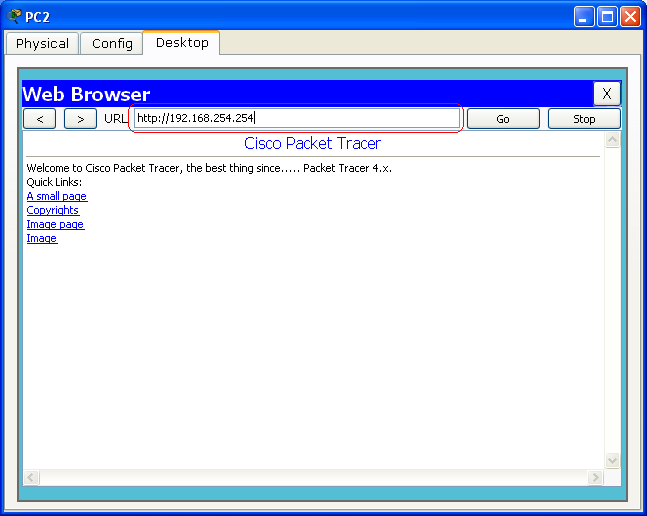
Click on PC2, Click Desktop tab, and under Desktop tab, click on the Web Browser icon. Under Web Browser, type 192.168.254.254 and press Enter key.
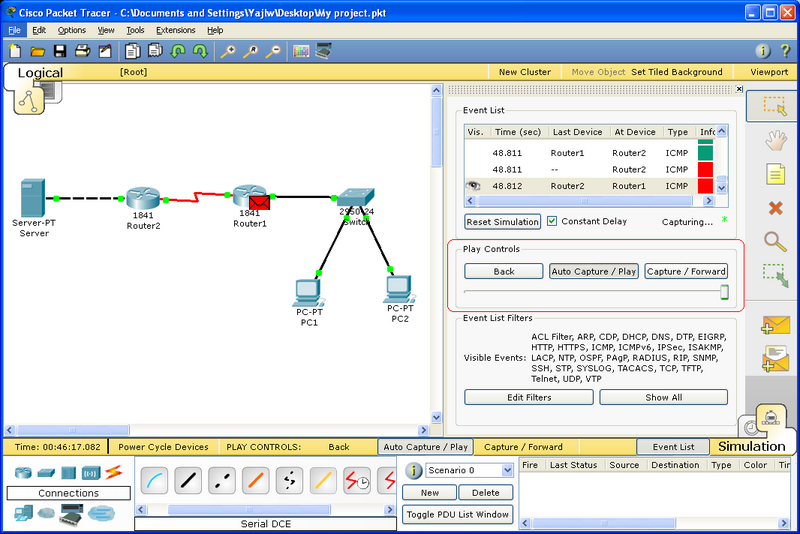
Simulation Mode
If you want to see how packets travel across the network, use the Simulation Mode.
To switch from Realtime Mode to Simulation Mode, click on the tab behind the Realtime Mode.
Simulation Mode:
The Simulation Mode lets you capture packets automatically or manually. Use Simulation Mode to capture packets by using ping and tracrt command or any other method to perform for the task.
Play Control of Simulation Mod
There are several methods to test network connectivity. However, I will not walk you through all the methods. Up to this point, you should know the basic operation of Cisco Packet Tracer, and be able to build your own network for your needed.
Enjoy!
--Lueyang 02:06, 1 March 2010 (UTC)