Multilayer Switching: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[File: | [[File:ODD.jpg ]] | ||
'''Optical Drive''' aka ODD (Optical Disc Drive) or CD/DVD Drive | '''Optical Drive''' aka ODD (Optical Disc Drive) or CD/DVD Drive | ||
Optical drives can be either internal or external and are used to read and/or write CD's, DVD's and Blu-ray discs depending on the specific drive. | Optical drives can be either internal or external and are used to read and/or write CD's, DVD's and Blu-ray discs depending on the specific drive. | ||
Revision as of 15:22, 29 July 2010
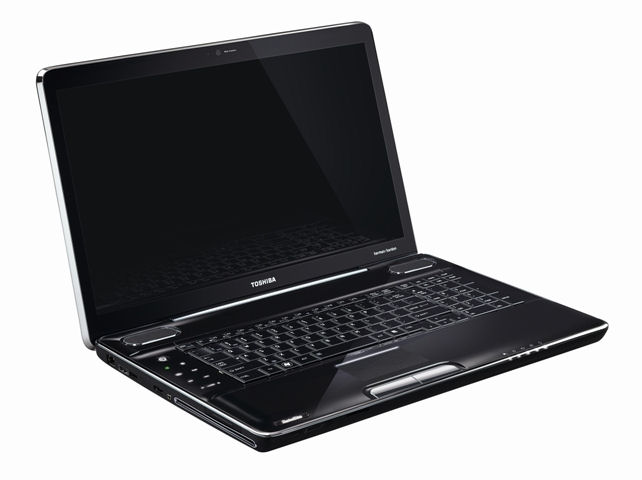
Parts In a Laptop
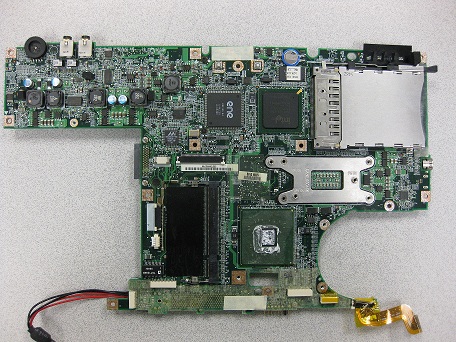 Motherboard
The motherboard is the board that all internal laptop components are connected to.
Motherboard
The motherboard is the board that all internal laptop components are connected to.
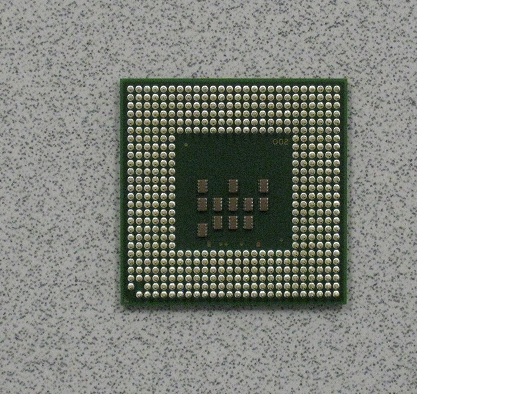
Processor aka CPU (Central ProcessingUnit)
The CPU is considered to be the brain of the computer which contains the circuitry used to interpret and execute program instructions.
 Memory aka RAM (Random Access Memory)
Memory is used for the temporary storage and manipulation of data, when a program is opened it is loaded into RAM for quick and easy access.
Memory aka RAM (Random Access Memory)
Memory is used for the temporary storage and manipulation of data, when a program is opened it is loaded into RAM for quick and easy access.
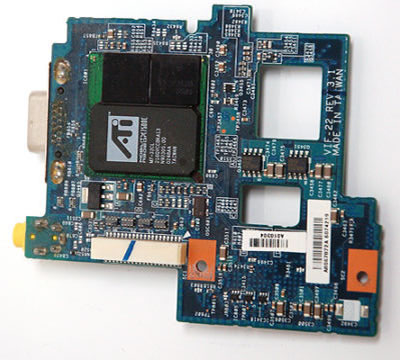 Video Card aka Graphics Card or Display Adapter
The graphics card is a circuit board that generates and outputs the images to be displayed on the lcd screen.
Video Card aka Graphics Card or Display Adapter
The graphics card is a circuit board that generates and outputs the images to be displayed on the lcd screen.
Audio Board aka Sound Board The audio board is used to enable the laptop to input, process, and output sound.
[[File:]]
Hard Drive aka HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
The hard disk drive is where you operating system, program files, and personal files are stored. Laptop hard drives are either 2.5" (60mm) or 1.8" (46mm) in size and thinner than desktop hard drives. The two most common hard drive interfaces in laptops are IDE/PATA (Integrated Drive Electronics/Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment) and SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment). Serial ATA is the replacement for the older Parallel ATA hard drives.
 Optical Drive aka ODD (Optical Disc Drive) or CD/DVD Drive
Optical drives can be either internal or external and are used to read and/or write CD's, DVD's and Blu-ray discs depending on the specific drive.
Optical Drive aka ODD (Optical Disc Drive) or CD/DVD Drive
Optical drives can be either internal or external and are used to read and/or write CD's, DVD's and Blu-ray discs depending on the specific drive.
Media:Screen.jpg
LCD Screen
The LCD (liquid-crystal display) screen uses liquid crystals, sealed between two polarizing filters, to redirect light when they are energized.
 Inverter Board aka FL Inverter
The inverter board provides power to the backlight lamp inside your LCD screen, which allows the image on the screen to be bright.
Inverter Board aka FL Inverter
The inverter board provides power to the backlight lamp inside your LCD screen, which allows the image on the screen to be bright.
LCD Cable aka Video Cable The LCD cable connects the motherboard to the LCD screen, so data can be transfered from the motherboard and video card to the screen.
 Touchpad aka Touch Mouse Pad
The touchpad on a laptop is an alternative to using a mouse.
Touchpad aka Touch Mouse Pad
The touchpad on a laptop is an alternative to using a mouse.
 AC Adapter
The AC adapter for a laptop connects to a power outlet to both provide electricity for your laptop and to charge your battery.
AC Adapter
The AC adapter for a laptop connects to a power outlet to both provide electricity for your laptop and to charge your battery.
 Main Battery aka Laptop Battery
The laptop battery powers your laptop when it is not plugged into a wall outlet via an AC adapter. Most laptop batteries need to replaced every 3 to 5 years depending on how often you use the laptop with only battery power.
Main Battery aka Laptop Battery
The laptop battery powers your laptop when it is not plugged into a wall outlet via an AC adapter. Most laptop batteries need to replaced every 3 to 5 years depending on how often you use the laptop with only battery power.
 CMOS Battery aka RTC (Real Time Clock) Battery
The CMOS battery provides power to the CMOS chip when the laptop is not powered on. The CMOS memory stores the date, time, and system setup parameters. Without the CMOS Battery, the CMOS would not be able to continuosly keep track of the date and time while your computer is off.
CMOS Battery aka RTC (Real Time Clock) Battery
The CMOS battery provides power to the CMOS chip when the laptop is not powered on. The CMOS memory stores the date, time, and system setup parameters. Without the CMOS Battery, the CMOS would not be able to continuosly keep track of the date and time while your computer is off.
 Heat Sink & Fan
Fans and heat sinks help in cooling down your laptop to prevent overheating. The heat sink is a device often made of copper or aluminum that sits on top of high heat generating chips such as the CPU and draws the heat away from the chip into the fins of the heat sink.
Heat Sink & Fan
Fans and heat sinks help in cooling down your laptop to prevent overheating. The heat sink is a device often made of copper or aluminum that sits on top of high heat generating chips such as the CPU and draws the heat away from the chip into the fins of the heat sink.