Linux VLAN Trunking: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (moved Linux VLan Trunking to Linux VLAN Trunking) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Step 4== | ==Step 4== | ||
Configure IP Addresses on the virtual interfaces. | Configure IP Addresses on the virtual interfaces. | ||
:ifconfig etho.10 | :ifconfig etho.10 ''ip address'' netmask ''subnet mask'' | ||
:[[File:Configvlanip.jpg|middle]] | :[[File:Configvlanip.jpg|middle]] | ||
| Line 43: | Line 40: | ||
Configure the default gateway for each virtual interface / VLAN | Configure the default gateway for each virtual interface / VLAN | ||
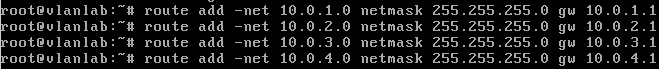
:route add -net | :route add -net ''ip address'' netmask ''subnet mask'' gw ''default gateway'' | ||
:[[File:Defaultroute.jpg|middle]] | :[[File:Defaultroute.jpg|middle]] | ||
;The server should now be trunking VLANS 10,20,30, and 40 | ;The server should now be trunking VLANS 10,20,30, and 40 on eth0 | ||
Revision as of 04:44, 7 May 2010
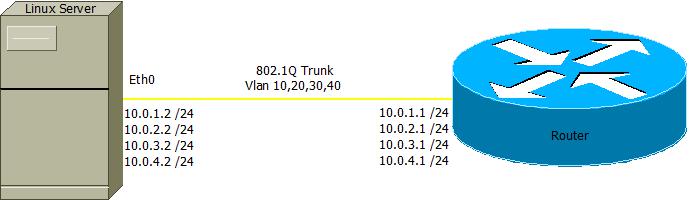
Basic VLAN Trunking in Debian based Linux.
Goals of Lab
- Enable 802.1Q Tagging
- Create Virtual Interfaces
Scenario
Step 1
The first thing you'll want to do is install the VLAN package using aptitude.
Note: if aptitude can't find the package, use the command "aptitude update" before trying to install the package.
Step 2
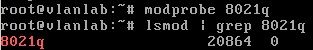
Load the 802.1Q module into the kernel
- sudo modprobe 8021q
Then verify the module has been loaded into the kernel
- lsmod | grep 8021q
The output on your screen should look similar:
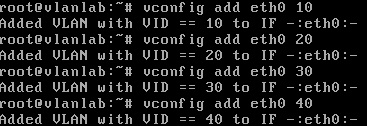
Step 3
Use vconfig to add virtual interfaces / VLANS
- vconfig add eth0 10
- vconfig add eth0 20
- vconfig add eth0 30
- vconfig add eth0 40
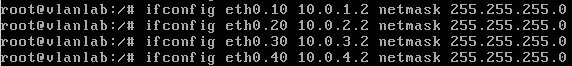
Step 4
Configure IP Addresses on the virtual interfaces.
- ifconfig etho.10 ip address netmask subnet mask
Step 5
Configure the default gateway for each virtual interface / VLAN
- route add -net ip address netmask subnet mask gw default gateway
- The server should now be trunking VLANS 10,20,30, and 40 on eth0