Cisco Wireless VoIP Configuration: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
'''Login.''' The wireless control web interface is managed through the address, 172.16.100.251 via SSL. | '''Login.''' The wireless control web interface is managed through the address, 172.16.100.251 via SSL. | ||
[[File:WLCM-login.jpg]] | |||
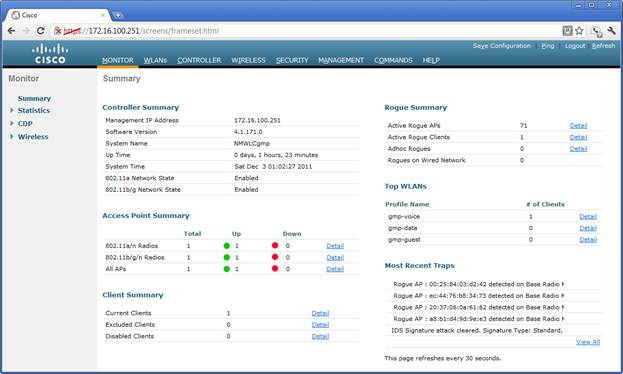
The primary screen summarizes the access points that are connected and wireless clients. In the screen image,below, one access point is connected and one client is connected to the gmp-voice SSID. The IHCC production access points and clients are considered to be ‘rogue’ to the controller. | The primary screen summarizes the access points that are connected and wireless clients. In the screen image,below, one access point is connected and one client is connected to the gmp-voice SSID. The IHCC production access points and clients are considered to be ‘rogue’ to the controller. | ||
[[File:WLCM-Summary.jpg]] | |||
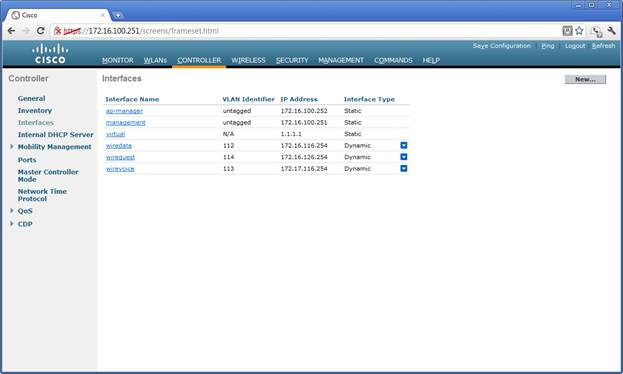
'''VLAN Interfaces.''' Each vlan is assigned an interface and an address. This is done through the “Controller interfaces” page. In the example, below, the interfaces are named wiredata, wireguest, wirevoice and have addresses, 172.16.116.254, 172.16.126.254, and 172.17.116.254, respectively. | '''VLAN Interfaces.''' Each vlan is assigned an interface and an address. This is done through the “Controller interfaces” page. In the example, below, the interfaces are named wiredata, wireguest, wirevoice and have addresses, 172.16.116.254, 172.16.126.254, and 172.17.116.254, respectively. | ||
[[File:WLCM-Controller-Interfaces.jpg]] | |||
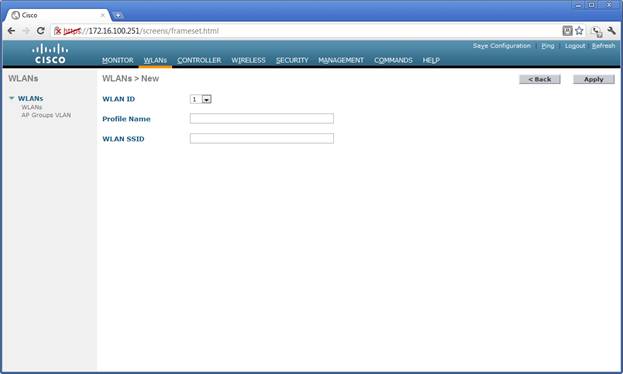
'''Wireless Profiles/SSIDs.''' Wireless profiles define the characteristics of the wireless SSID. The following image shows the creation page for a new SSID. The WLAN ID is a unique identifier within the controller. The profile name and SSID are text strings.. | '''Wireless Profiles/SSIDs.''' Wireless profiles define the characteristics of the wireless SSID. The following image shows the creation page for a new SSID. The WLAN ID is a unique identifier within the controller. The profile name and SSID are text strings.. | ||
[[File:WLCM-New-WLAN.jpg]] | |||
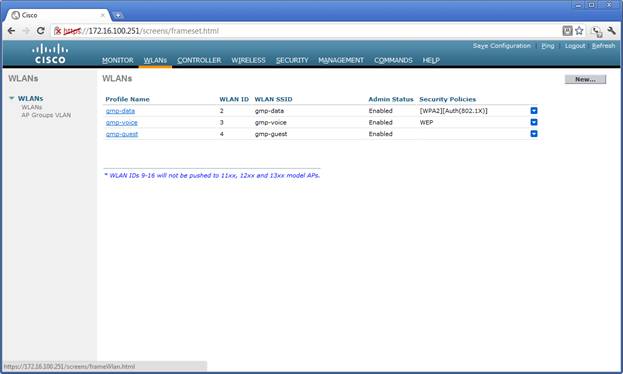
The following image shows the three profiles and SSIDs. Here the profile and the SSIDs have the same name. | The following image shows the three profiles and SSIDs. Here the profile and the SSIDs have the same name. | ||
[[File:WLCM-WLANs.jpg]] | |||
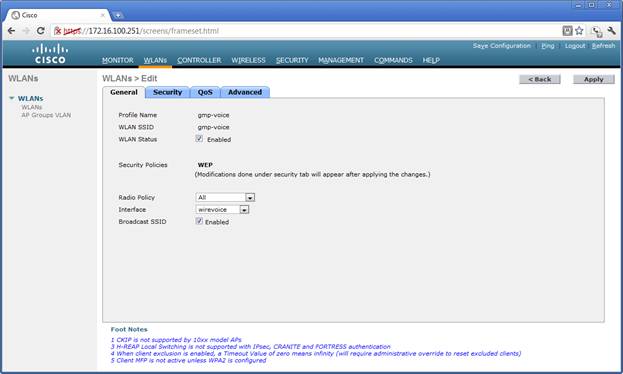
'''Voice SSID.''' The image shows that the profile and SSID, gmp-voice, is associated with the wirevoice interface. Wirevoice is vlan 113 with address 172.17.116.0/24. | '''Voice SSID.''' The image shows that the profile and SSID, gmp-voice, is associated with the wirevoice interface. Wirevoice is vlan 113 with address 172.17.116.0/24. | ||
[[File:WLCM-gmp-voice-General.jpg]] | |||
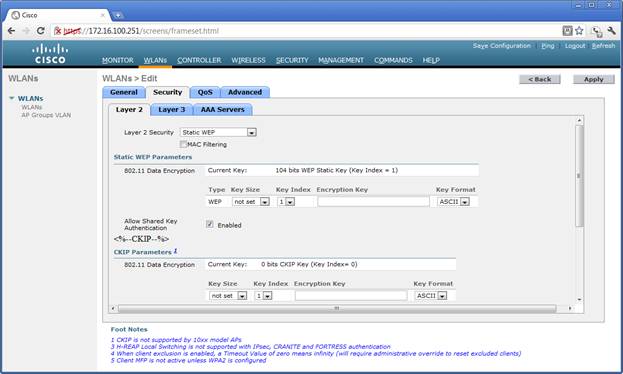
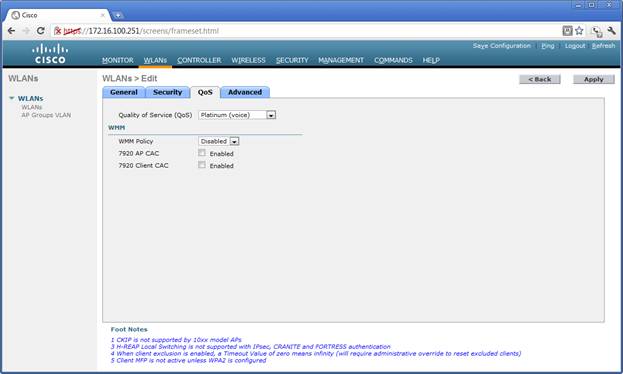
The following pages illustrate the Security, QOS, and Advanced configuration options. | The following pages illustrate the Security, QOS, and Advanced configuration options. | ||
[[File:WLCM-wlan-Security.jpg]] | |||
[[File:WLCM-wlan-QoS.jpg]] | |||
[[File:WLCM-wlan-Advanced.jpg]] | |||
====Wireless Controller Configuration -- CLI==== | ====Wireless Controller Configuration -- CLI==== | ||
Latest revision as of 02:03, 3 December 2011
G. Polanski VOIP Project CNT-2722-01 Foundations of IP Telephony
Purpose: The purpose of this project is to demonstrate the use of a Cisco 7921G Wireless phone. The activity includes the following components.
- Cisco Call Manager Express
- Cisco Wireless Lan Controller and Cisco 1242 access point
- Cisco 7921G wireless phone
- Cisco 3560 Switch
Demonstration. The functionality of the application is demonstrated by establishing calls between the wireless phone, x7616, a VOIP phone, x7618, and an analog phone, x6007.
VLANS
Five VLANs are used to emulate a business environment. Two wired vlans support voice and data. Three wireless vlans support wireless data, wireless voice, and a guest wireless network. A sixth vlan is used to configure the Wireless LAN Controller. The vlans and address values are listed below.
- 100 Wireless Mgmt Vlan 172.16.100.0/24
- 110 Data VLAN 172.16.106.0/24
- 111 Voice VLAN 172.17.106.0/24
- 112 Wireless Data VLAN 172.16.116.0/24
- 113 Wireless Voice VLAN 172.17.116.0/24
- 114 Wireless Guest VLAN 172.16.126.0/24
Layer 3 Switch
The Cisco 3560 switch, TELSW1-DLS1, provides layer 3 routing to the wired vlans, and POE to the access point and to the Cisco IP Phones. The switch is connected to the router via a routed port. EIGRP is used as the routing protocol in the switch and the router. The router is the DHCP server, so the switch is configured with an IP helper address to forward the DHCP requests to the router.
Port Configuration
The following text summarizes the port configuration in the 3560 switch. The phrase, "mls qos", enables Cisco quality of service in the 3560 switch. The phrase, "auto qos voip cisco-phone", enables QoS on the access ports. These phrases correspond to Activity 7.7, IP Telephony QoS Considerations.
mls qos interface range FastEthernet0/1 - 23 description End user data ports switchport access vlan 110 switchport mode access switchport voice vlan 111 srr-queue bandwidth share 10 10 60 20 priority-queue out mls qos trust device cisco-phone mls qos trust cos auto qos voip cisco-phone spanning-tree portfast service-policy input AutoQoS-Police-CiscoPhone ! interface FastEthernet0/24 description Connect to 2811 Router port fa 0/1 on Router no switchport ip address 172.16.252.2 255.255.255.252 srr-queue bandwidth share 10 10 60 20 priority-queue out mls qos trust dscp auto qos voip trust spanning-tree portfast !
Switch DHCP Configuration
DHCP services are provided by the router. The DHCP configuration in the switch include a helper address. As a result, the DHCP requests are forwarded to the router. The two vlans, below, support the data vlan and the voice vlan in the switch. The address is the loopback address of the router.
interface Vlan110 description Wired Data ip address 172.16.106.1 255.255.255.0 ip helper-address 172.16.251.1 ! interface Vlan111 description Wired Voice ip address 172.17.106.1 255.255.255.0 ip helper-address 172.16.251.1 !
Router
The router provides several functions.
- Cisco Call Manager Express. The CME module controls both the wired phones and the wireless phone.
- DHCP. The router is configured to provide DHCP addresses to the wired and wireless vlans.
- NTP. The router is the NTP master.
- Wireless LAN Controller. The WLAN controller is a module in the switch.
Cisco Call Manager Express
The following text begins the call manager configuration. The IP address is the loopback address in the router.
! Define telephony service on Call Manager Express ! telephony-service max-ephones 12 max-dn 24 ip source-address 172.16.251.1 port 2000 timeouts interdigit 3 load 7960-7940 P00307020200 time-zone 8 max-conferences 8 gain -6 transfer-system full-consult create cnf-files version-stamp 7960 Nov 02 2011 14:13:27 !
The ephone-dn phrases define a phone number and a directory entry. The ephone statements identify the physical phones by MAC address and phone type. The button statement associates the phone number with the button on the phone.
Wireless Phone. The wireless phone definition follows. The phone is extension 7616.
ephone-dn 16 number 7616 name POD6-IP-7616 ! ephone 6 mac-address 0022.90fd.d1e7 type 7921 button 1:16
Wired Phone. The wired Cisco IP Phone definition follows. The wired phone is extension 7618.
ephone-dn 18 number 7618 name POD6-IP-7618 ! ephone 8 device-security-mode none mac-address 001B.5452.5FC9 type 7941 button 1:18 !
Analog Phone. An analog phone is connected to port 0 of and FXS WIC. The analog phone is extension 6007.
voice-port 0/1/0 description FXs WIC to Analog phone ! dial-peer voice 1 pots description FXS WIC with Analog Phone 6007 destination-pattern 6007 port 0/1/0 !
DHCP
The following configuration defines the DHCP services for the devices.
- The lease parameters are Days, Hours, Minutes. The wired devices have a lease for one day. The wireless leases are only 6 hours.
- Option 43 is the access point contact address in the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller. When the lightweight access point is connected to the network, the access point contacts the controller. The first four characters are "f104" The following characters represent the IP address in hexadecimal. 0xAC = 172, 0x10 = 16, 0x64 = 100, 0xFC=252
- Option 150 is the tftp server address for the Cisco IP Phones.
ip dhcp pool Data-Devices
! description 172.16.100.252 is hex f104ac1064gfc
network 172.16.106.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 172.16.106.1
option 43 hex f104ac1064fc
lease 1 0 0
class Data
address range 172.16.106.50 172.16.106.254
ip dhcp pool Voice-Devices
network 172.17.106.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 172.17.106.1
lease 1 0 0
option 150 ip 172.16.251.1
class Voice
address range 172.17.106.50 172.17.106.254
ip dhcp pool Wireless-Data
network 172.16.116.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 172.16.116.1
lease 0 6 0
class Data
address range 172.16.116.50 172.16.116.254
ip dhcp pool Wireless-Voice
network 172.17.116.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 172.17.116.1
lease 0 6 0
class Voice
address range 172.17.116.50 172.17.116.254
ip dhcp pool Wireless-Guest
network 172.17.116.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 172.16.126.1
lease 0 6 0
class Data
address range 172.16.126.50 172.16.126.254
NTP Master
The router has a system calendar, which continues to run even when the router is off. The calendar is set through a command that is similar to the clock set command; "calendar set hh:mm:ss day month year". In the lab environment, the router may be used as the NTP server.
The router is set as the NTP server via the following command
ntp master 10
The switch references the NTP server via
ntp server 172.16.251.1
Wireless LAN Controller
The Cisco Wireless LAN Controller is a module in the router. The controller manages a Cisco 1242 access point as a lightweight AP. The access point tunnels all traffic back to the wireless controller. Three SSIDs are used.
- gmp-voice
- gmp-data
- gmp-guest
Wireless Controller Configuration -- Trunked
Since the wireless networks support data, voice, and guest networks, the wireless controller connects to the router via a trunked port. Each SSID in the wireless environment is a different vlan. The following configuration shows the trunking and the subinterfaces in the router.
interface wlan-controller1/0 ip address 172.16.100.254 255.255.255.0 ! interface wlan-controller1/0.112 description Wireless Data encapsulation dot1Q 112 ip address 172.16.116.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface wlan-controller1/0.113 description Wireless Voice encapsulation dot1Q 113 ip address 172.17.116.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface wlan-controller1/0.114 description Wireless-Guest encapsulation dot1Q 114 ip address 172.16.126.1 255.255.255.0 !
Wireless Controller Configuration – GUI
Login. The wireless control web interface is managed through the address, 172.16.100.251 via SSL.
The primary screen summarizes the access points that are connected and wireless clients. In the screen image,below, one access point is connected and one client is connected to the gmp-voice SSID. The IHCC production access points and clients are considered to be ‘rogue’ to the controller.
VLAN Interfaces. Each vlan is assigned an interface and an address. This is done through the “Controller interfaces” page. In the example, below, the interfaces are named wiredata, wireguest, wirevoice and have addresses, 172.16.116.254, 172.16.126.254, and 172.17.116.254, respectively.
Wireless Profiles/SSIDs. Wireless profiles define the characteristics of the wireless SSID. The following image shows the creation page for a new SSID. The WLAN ID is a unique identifier within the controller. The profile name and SSID are text strings..
The following image shows the three profiles and SSIDs. Here the profile and the SSIDs have the same name.
Voice SSID. The image shows that the profile and SSID, gmp-voice, is associated with the wirevoice interface. Wirevoice is vlan 113 with address 172.17.116.0/24.
The following pages illustrate the Security, QOS, and Advanced configuration options.
Wireless Controller Configuration -- CLI
The initial setup of the controller begins with the command line interface. Cisco Document 70530, "Wireless LAN Controller Module (WLCM) Configuration Examples" has several examples for the initial configuration of the WLCM.
Since the controller is a service module, the module is accessed via the service-module command
TELRTR1#service-module wlan-controller 1/0 session Trying 172.16.100.254, 2066 ... Open C Warning! Authorized Access Only! User:admin Password:***** (Cisco Controller) >?
The sessions is disconnected via CTRL-Shift-6 and the disconnect command.
(Cisco Controller) User: CTRL-SHIFT-6 TELRTR1#show session Conn Host Address Byte Idle Conn Name * 1 172.16.100.254 172.16.100.254 0 0 172.16.100.254 TELRTR1#disconnect 1 Closing connection to 172.16.100.254 [confirm] TELRTR1#
Wireless Controller Configuration
The wireless controller configuration for this activity is shown below.
(Cisco Controller) >show running-config 802.11a cac voice tspec-inactivity-timeout ignore 802.11a cac voice stream-size 84000 max-streams 2 802.11a channel global off 802.11a txPower global 1 802.11b cac voice tspec-inactivity-timeout ignore 802.11b cac voice stream-size 84000 max-streams 2 802.11b channel global off 802.11b txPower global 1 advanced location expiry tags 1200 advanced location expiry client 150 advanced location expiry calibrating-client 30 advanced location expiry rogue-aps 1200 cdp disable interface create wiredata 112 interface create wireguest 114 interface create wirevoice 113 interface address ap-manager 172.16.100.252 255.255.255.0 172.16.100.254 interface address management 172.16.100.251 255.255.255.0 172.16.100.254 interface address virtual 1.1.1.1 interface address dynamic-interface wiredata 172.16.116.254 255.255.255.0 172.16.116.1 interface address dynamic-interface wireguest 172.16.126.254 Z55.255.255.0 172.16.126.1 interface address dynamic-interface wirevoice 172.17.116.254 255.255.255.0 172.17.116.1 interface dhcp ap-manager primary 172.16.100.251 interface dhcp management primary 172.16.100.251 interface dhcp dynamic-interface wiredata primary 172.16.251.1 interface dhcp dynamic-interface wireguest primary 172.16.251.1 interface dhcp dynamic-interface wirevoice primary 172.16.251.1 interface vlan wiredata 112 interface vlan wireguest 114 interface vlan wirevoice 113 interface port ap-manager 1 interface port management 1 interface port wiredata 1 interface port wireguest 1 interface port wirevoice 1 logging buffered 1 mesh security eap mgmtuser add admin **** read-write mobility group domain mg1 msglog level critical network rf-network-name mg1 snmp version v2c enable snmp version v3 enable sysname NMWLCgmp time ntp server 1 172.16.251.1 wlan create 2 gmp-data gmp-data wlan create 3 gmp-voice gmp-voice wlan create 4 gmp-guest gmp-guest wlan interface 2 wiredata wlan interface 3 wirevoice wlan interface 4 wireguest wlan qos 3 platinum wlan security static-wep-key enable 3 wlan security static-wep-key authentication shared-key 3 wlan security static-wep-key encryption 2 104 ascii **** 1 wlan security static-wep-key encryption 3 104 ascii **** 1 wlan security wpa disable 3 wlan security wpa disable 4 wlan security wpa wpa1 ciphers tkip enable 2 wlan enable 2 wlan enable 3 wlan enable 4