Cracking WEP: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
| [[Image:wrt54g.jpg|thumb|upright|Linksys wireless router(WRT54G)|202px]] | | [[Image:wrt54g.jpg|thumb|upright|Linksys wireless router(WRT54G)|202px]] | ||
| [[Image:bt_screenshot.jpg|thumb|upright|A screenshot of BackTrack 3|230px]] | | [[Image:bt_screenshot.jpg|thumb|upright|A screenshot of BackTrack 3|230px]] | ||
| [[Image:alfa.jpg|thumb|upright|Alfa | | [[Image:alfa.jpg|thumb|upright|Alfa AWUS036H|108px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Capturing Packets== | ==Capturing Packets== | ||
[[Image:bt01.jpg|thumb|Selecting Wireless Assistant.]] | [[Image:bt01.jpg|thumb|Selecting Wireless Assistant.|250px]] | ||
:Follow the steps bellow to setup and capture packets using BackTrack 3. | :Follow the steps bellow to setup and capture packets using BackTrack 3. | ||
===Checking the Adapter=== | |||
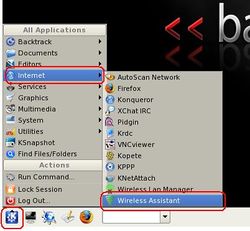
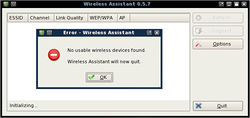
:*On the Sniffing PC that is running BackTrack 3, select the small '''K''' icon located on the lower left hand corner. Select '''Internet''' and then click on '''Wireless Assistant'''. | :*On the Sniffing PC that is running BackTrack 3, select the small '''K''' icon located on the lower left hand corner. Select '''Internet''' and then click on '''Wireless Assistant'''. When the '''Wireless Assistant''' window appear, you should see the target wireless access point that you want to hack. If you don’t have a compatible wireless adapter, it will prompt you an error massage says “No usable wireless device found.” | ||
{| | {| | ||
| [[Image:bt02.jpg|thumb|upright|If the device is compatible|300px]] | | [[Image:bt02.jpg|thumb|upright|If the device is compatible|300px]] | ||
| Line 42: | Line 40: | ||
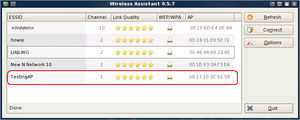
:Take note some of the information such as the BSSID, the channel number, and the MAC address of the wireless access point that you want to crack. In this lab, the SSID is Testing AR on channel 1, and MAC address is 00:13:10:3C:51:5B. When you done, close the Wireless Assistant window. | :Take note some of the information such as the BSSID, the channel number, and the MAC address of the wireless access point that you want to crack. In this lab, the SSID is Testing AR on channel 1, and MAC address is 00:13:10:3C:51:5B. When you done, close the Wireless Assistant window. | ||
===1st Shell - Konsole Window=== | |||
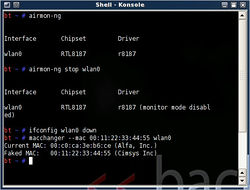
[[Image:bt04.jpg|thumb|Results of the commands.|250px]] | |||
:*Run Shell – Konsole window. It is a small black screen icon located on the lower left hand corner next to the small K icon. | :*Run Shell – Konsole window. It is a small black screen icon located on the lower left hand corner next to the small K icon. | ||
:*Enter the command bellow to find the adapter name. Once the name of your wireless adapter shown, take note of the interface name. Mine is wlan0. | :*Enter the command bellow to find the adapter name. Once the name of your wireless adapter shown, take note of the interface name. Mine is wlan0. | ||
airmon-ng | airmon-ng | ||
:*Enter the 4 commands bellow by typing each command and press Enter key. | :*Enter the 4 commands bellow by typing each command and press Enter key. | ||
airmon-ng stop '' | airmon-ng stop ''<your device Interface>'' | ||
ifconfig '' | ifconfig ''<your device Interface>'' down | ||
macchanger --mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 '' | macchanger --mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 ''<your device Interface>'' | ||
airmon-ng start '' | airmon-ng start ''<your device Interface>'' | ||
:The purpose of these commands is to change the MAC Address of your wireless adapter to a faked MAC Address: 00:11:22:33:44:55. | :The purpose of these commands is to change the MAC Address of your wireless adapter to a faked MAC Address: 00:11:22:33:44:55. | ||
| Line 59: | Line 56: | ||
:All the result of the commands above should look like the screenshot on the right. | :All the result of the commands above should look like the screenshot on the right. | ||
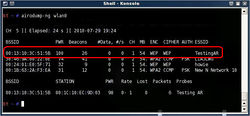
[[Image:bt05.jpg|thumb|List of wireless access points around.|250px]] | |||
:*Run the command bellow to see a list of the wireless access points around you. | |||
airodump-ng ''<your device Interface>'' | |||
:*Once you see the Target AP, press Ctrl+C to stop scanning. On the list, you will see information such as the MAC Address (BSSID), power level, channel, encryption protocol, and the name of the access point (ESSID) of each device. Write down this information of the wireless access point that you are going to hack for later use. The Target AP used in this lab is the highlighted in red in the snapshot on the right. | |||
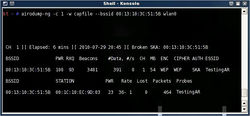
: | [[Image:bt06.jpg|thumb|Capturing packets traffic.|250px]] | ||
:*Run the command bellow. This command will capture the packets traffic between the Target AP and any wireless client. | |||
airodump-ng -c ''<channel>'' -w ''<file name>'' --bssid ''<BSSID> <your device interface>'' | |||
:'''Note:''' The channel, BSSID, and your device interface is the information that you noted above. The file name can be any name you want. Here I used capfile as the file name. The command I used and the output is shown on the snapshot on the right. | |||
:* | :*Now, I will use the second laptop (the Target PC) to watch some movies on youtube to generate more traffic between the Target AP and Target PC. Remember that the more packets traffic to the wireless access point, the more packets you can capture, and the more likely you will successfully crack the WEP key faster. | ||
===2nd Shell - Konsole Window=== | |||
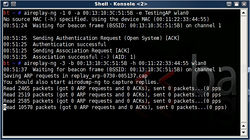
[[Image:bt07.jpg|thumb|Creating traffic snapshot.|250px]] | |||
:*Open a new Shell – Konsole windows without closing the first Shell - Konsole window. | |||
:*Enter the following command to speed up the process. | |||
aireplay-ng -1 0 -a ''<BSSID>'' -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 -e ''<ESSID> <your device interface>''. | |||
: | :In this lab, the BSSID is the MAC Address of my wireless router (00:13:10:3C:51:5B), and the ESSID is the name of the access point (TestingAP). | ||
:*Enter the command bellow to generate more packets traffic. | |||
aireplay-ng -3 -b ''<BSSID>'' -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 ''<your interface name>'' | |||
:These two commands are supposed to speed the process and the the traffic | |||
: | :'''NOTE:'''You should wait until enough packets (data) has been captured before you run the cracking command bellow; otherwise it will not work. Look at the number of packets captured on the firs Shell - Konsole window. This is the number right bellow the #data column. Wait until this number goes above 10000, and then process to the cracking step bellow. | ||
==Cracking the WEP key== | |||
===3rd Shell - Konsole Window=== | |||
This is the final and the actual step to get the WEP key. | |||
==Conclusion== | ==Conclusion== | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 30 July 2010
- In this lab, I will show you how to crack WEP using BackTrack 3. As you may know, WEP is a week security protocol that can be broken easily. There are dozens of articles about cracking WEP on the internet, so if this article doesn’t give you enough information, please do some online researches. The purpose of this lab is not encouraged you to be a hacker. I set this lab for educational purpose and to prove that WEP is a weak protocol that can be hacked easily.
Hardware required
Here is a list of equipment and hardware Requirement for this lab:
- A wireless router - this could be any wireless router that supported WEP security encryption.
- A BackTrack 3 Live CD
- 2 wireless adapters - one of them should be a compatible wireless adapter.
- At least 2 PCs – In this lab, I used a desktop and a laptop. I installed the compatible wireless adapter card in the desktop, and the other laptop has a build-in wireless adapter.
Setup the Wireless Lab
- Bellow are the software and hardware I used to this lab.
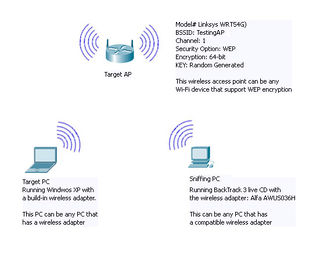
- The wireless router: I used the Linksys wireless router (WRT54G) as the wireless access point. I setup the wireless router as shown in the snapshot bellow.
- The BackTrack 3 Live CD can be downloaded at http://www.backtrack-linux.org/downloads/. After the ISO image file has been downloaded, I burn it into a blank CD. If you would like instruction information of how to burn an ISO file to a CD/DVD, click on this link http://pcsupport.about.com/od/toolsofthetrade/ht/burnisofile.htm.
- Find a compatible wireless adapter from http://www.aircrack-ng.org/doku.php?id=compatibility_drivers#compatibility. Find one and buy it or use the one that you have. The wireless adapter I used in this lab was the Alfa AWUS036H. I bought it online for $29.
- I inserted the Alfa AWUS036H wireless adapter into an USB port on my desktop and insert the BackTrack 3 Live CD into the CD ROM. I called this desktop the “Sniffing PC.” Boot the Sniffing PC from the CD.
- I made sure that the laptop (the Target PC) and the wireless router WRT54G (the Target AP) are configured and communicated with each other correctly.
Capturing Packets
- Follow the steps bellow to setup and capture packets using BackTrack 3.
Checking the Adapter
- On the Sniffing PC that is running BackTrack 3, select the small K icon located on the lower left hand corner. Select Internet and then click on Wireless Assistant. When the Wireless Assistant window appear, you should see the target wireless access point that you want to hack. If you don’t have a compatible wireless adapter, it will prompt you an error massage says “No usable wireless device found.”
- Take note some of the information such as the BSSID, the channel number, and the MAC address of the wireless access point that you want to crack. In this lab, the SSID is Testing AR on channel 1, and MAC address is 00:13:10:3C:51:5B. When you done, close the Wireless Assistant window.
1st Shell - Konsole Window
- Run Shell – Konsole window. It is a small black screen icon located on the lower left hand corner next to the small K icon.
- Enter the command bellow to find the adapter name. Once the name of your wireless adapter shown, take note of the interface name. Mine is wlan0.
airmon-ng
- Enter the 4 commands bellow by typing each command and press Enter key.
airmon-ng stop <your device Interface> ifconfig <your device Interface> down macchanger --mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 <your device Interface> airmon-ng start <your device Interface>
- The purpose of these commands is to change the MAC Address of your wireless adapter to a faked MAC Address: 00:11:22:33:44:55.
- All the result of the commands above should look like the screenshot on the right.
- Run the command bellow to see a list of the wireless access points around you.
airodump-ng <your device Interface>
- Once you see the Target AP, press Ctrl+C to stop scanning. On the list, you will see information such as the MAC Address (BSSID), power level, channel, encryption protocol, and the name of the access point (ESSID) of each device. Write down this information of the wireless access point that you are going to hack for later use. The Target AP used in this lab is the highlighted in red in the snapshot on the right.
- Run the command bellow. This command will capture the packets traffic between the Target AP and any wireless client.
airodump-ng -c <channel> -w <file name> --bssid <BSSID> <your device interface>
- Note: The channel, BSSID, and your device interface is the information that you noted above. The file name can be any name you want. Here I used capfile as the file name. The command I used and the output is shown on the snapshot on the right.
- Now, I will use the second laptop (the Target PC) to watch some movies on youtube to generate more traffic between the Target AP and Target PC. Remember that the more packets traffic to the wireless access point, the more packets you can capture, and the more likely you will successfully crack the WEP key faster.
2nd Shell - Konsole Window
- Open a new Shell – Konsole windows without closing the first Shell - Konsole window.
- Enter the following command to speed up the process.
aireplay-ng -1 0 -a <BSSID> -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 -e <ESSID> <your device interface>.
- In this lab, the BSSID is the MAC Address of my wireless router (00:13:10:3C:51:5B), and the ESSID is the name of the access point (TestingAP).
- Enter the command bellow to generate more packets traffic.
aireplay-ng -3 -b <BSSID> -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 <your interface name>
- These two commands are supposed to speed the process and the the traffic
- NOTE:You should wait until enough packets (data) has been captured before you run the cracking command bellow; otherwise it will not work. Look at the number of packets captured on the firs Shell - Konsole window. This is the number right bellow the #data column. Wait until this number goes above 10000, and then process to the cracking step bellow.
Cracking the WEP key
3rd Shell - Konsole Window
This is the final and the actual step to get the WEP key.